Busy Developers' Guide to Features
Want to use HSSF and XSSF read and write spreadsheets in a hurry? This guide is for you. If you're after more in-depth coverage of the HSSF and XSSF user-APIs, please consult the HOWTO guide as it contains actual descriptions of how to use this stuff.
Index of Features
Features
New Workbook
Workbook wb = new HSSFWorkbook();
FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream("workbook.xls");
wb.write(fileOut);
fileOut.close();
Workbook wb = new XSSFWorkbook();
FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream("workbook.xlsx");
wb.write(fileOut);
fileOut.close();
New Sheet
Workbook wb = new HSSFWorkbook(); // or new XSSFWorkbook();
Sheet sheet1 = wb.createSheet("new sheet");
Sheet sheet2 = wb.createSheet("second sheet");
// Note that sheet name is Excel must not exceed 31 characters
// and must not contain any of the any of the following characters:
// 0x0000
// 0x0003
// colon (:)
// backslash (\)
// asterisk (*)
// question mark (?)
// forward slash (/)
// opening square bracket ([)
// closing square bracket (])
// You can use org.apache.poi.ss.util.WorkbookUtil#createSafeSheetName(String nameProposal)}
// for a safe way to create valid names, this utility replaces invalid characters with a space (' ')
String safeName = WorkbookUtil.createSafeSheetName("[O'Brien's sales*?]"); // returns " O'Brien's sales "
Sheet sheet3 = wb.createSheet(safeName);
FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream("workbook.xls");
wb.write(fileOut);
fileOut.close();
Creating Cells
Workbook wb = new HSSFWorkbook();
//Workbook wb = new XSSFWorkbook();
CreationHelper createHelper = wb.getCreationHelper();
Sheet sheet = wb.createSheet("new sheet");
// Create a row and put some cells in it. Rows are 0 based.
Row row = sheet.createRow((short)0);
// Create a cell and put a value in it.
Cell cell = row.createCell(0);
cell.setCellValue(1);
// Or do it on one line.
row.createCell(1).setCellValue(1.2);
row.createCell(2).setCellValue(
createHelper.createRichTextString("This is a string"));
row.createCell(3).setCellValue(true);
// Write the output to a file
FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream("workbook.xls");
wb.write(fileOut);
fileOut.close();
Creating Date Cells
Workbook wb = new HSSFWorkbook();
//Workbook wb = new XSSFWorkbook();
CreationHelper createHelper = wb.getCreationHelper();
Sheet sheet = wb.createSheet("new sheet");
// Create a row and put some cells in it. Rows are 0 based.
Row row = sheet.createRow(0);
// Create a cell and put a date value in it. The first cell is not styled
// as a date.
Cell cell = row.createCell(0);
cell.setCellValue(new Date());
// we style the second cell as a date (and time). It is important to
// create a new cell style from the workbook otherwise you can end up
// modifying the built in style and effecting not only this cell but other cells.
CellStyle cellStyle = wb.createCellStyle();
cellStyle.setDataFormat(
createHelper.createDataFormat().getFormat("m/d/yy h:mm"));
cell = row.createCell(1);
cell.setCellValue(new Date());
cell.setCellStyle(cellStyle);
//you can also set date as java.util.Calendar
cell = row.createCell(2);
cell.setCellValue(Calendar.getInstance());
cell.setCellStyle(cellStyle);
// Write the output to a file
FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream("workbook.xls");
wb.write(fileOut);
fileOut.close();
Working with different types of cells
Workbook wb = new HSSFWorkbook();
Sheet sheet = wb.createSheet("new sheet");
Row row = sheet.createRow((short)2);
row.createCell(0).setCellValue(1.1);
row.createCell(1).setCellValue(new Date());
row.createCell(2).setCellValue(Calendar.getInstance());
row.createCell(3).setCellValue("a string");
row.createCell(4).setCellValue(true);
row.createCell(5).setCellType(Cell.CELL_TYPE_ERROR);
// Write the output to a file
FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream("workbook.xls");
wb.write(fileOut);
fileOut.close();
Files vs InputStreams
When opening a workbook, either a .xls HSSFWorkbook, or a .xlsx XSSFWorkbook, the Workbook can be loaded from either a File or an InputStream. Using a File object allows for lower memory consumption, while an InputStream requires more memory as it has to buffer the whole file.
If using WorkbookFactory, it's very easy to use one or the other:
// Use a file
Workbook wb = WorkbookFactory.create(new File("MyExcel.xls"));
// Use an InputStream, needs more memory
Workbook wb = WorkbookFactory.create(new FileInputStream("MyExcel.xlsx"));
If using HSSFWorkbook or XSSFWorkbook directly, you should generally go through NPOIFSFileSystem or OPCPackage, to have full control of the lifecycle (including closing the file when done):
// HSSFWorkbook, File
NPOIFSFileSytem fs = new NPOIFSFileSystem(new File("file.xls"));
HSSFWorkbook wb = new HSSFWorkbook(fs.getRoot());
....
fs.close();
// HSSFWorkbook, InputStream, needs more memory
NPOIFSFileSytem fs = new NPOIFSFileSystem(myInputStream);
HSSFWorkbook wb = new HSSFWorkbook(fs.getRoot());
// XSSFWorkbook, File
OPCPackage pkg = OPCPackage.open(new File("file.xlsx"));
XSSFWorkbook wb = new XSSFWorkbook(pkg);
....
pkg.close();
// XSSFWorkbook, InputStream, needs more memory
OPCPackage pkg = OPCPackage.open(myInputStream);
XSSFWorkbook wb = new XSSFWorkbook(pkg);
....
pkg.close();
Demonstrates various alignment options
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Workbook wb = new XSSFWorkbook(); //or new HSSFWorkbook();
Sheet sheet = wb.createSheet();
Row row = sheet.createRow((short) 2);
row.setHeightInPoints(30);
createCell(wb, row, (short) 0, CellStyle.ALIGN_CENTER, CellStyle.VERTICAL_BOTTOM);
createCell(wb, row, (short) 1, CellStyle.ALIGN_CENTER_SELECTION, CellStyle.VERTICAL_BOTTOM);
createCell(wb, row, (short) 2, CellStyle.ALIGN_FILL, CellStyle.VERTICAL_CENTER);
createCell(wb, row, (short) 3, CellStyle.ALIGN_GENERAL, CellStyle.VERTICAL_CENTER);
createCell(wb, row, (short) 4, CellStyle.ALIGN_JUSTIFY, CellStyle.VERTICAL_JUSTIFY);
createCell(wb, row, (short) 5, CellStyle.ALIGN_LEFT, CellStyle.VERTICAL_TOP);
createCell(wb, row, (short) 6, CellStyle.ALIGN_RIGHT, CellStyle.VERTICAL_TOP);
// Write the output to a file
FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream("xssf-align.xlsx");
wb.write(fileOut);
fileOut.close();
}
/**
* Creates a cell and aligns it a certain way.
*
* @param wb the workbook
* @param row the row to create the cell in
* @param column the column number to create the cell in
* @param halign the horizontal alignment for the cell.
*/
private static void createCell(Workbook wb, Row row, short column, short halign, short valign) {
Cell cell = row.createCell(column);
cell.setCellValue("Align It");
CellStyle cellStyle = wb.createCellStyle();
cellStyle.setAlignment(halign);
cellStyle.setVerticalAlignment(valign);
cell.setCellStyle(cellStyle);
}
Working with borders
Workbook wb = new HSSFWorkbook();
Sheet sheet = wb.createSheet("new sheet");
// Create a row and put some cells in it. Rows are 0 based.
Row row = sheet.createRow(1);
// Create a cell and put a value in it.
Cell cell = row.createCell(1);
cell.setCellValue(4);
// Style the cell with borders all around.
CellStyle style = wb.createCellStyle();
style.setBorderBottom(CellStyle.BORDER_THIN);
style.setBottomBorderColor(IndexedColors.BLACK.getIndex());
style.setBorderLeft(CellStyle.BORDER_THIN);
style.setLeftBorderColor(IndexedColors.GREEN.getIndex());
style.setBorderRight(CellStyle.BORDER_THIN);
style.setRightBorderColor(IndexedColors.BLUE.getIndex());
style.setBorderTop(CellStyle.BORDER_MEDIUM_DASHED);
style.setTopBorderColor(IndexedColors.BLACK.getIndex());
cell.setCellStyle(style);
// Write the output to a file
FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream("workbook.xls");
wb.write(fileOut);
fileOut.close();
Iterate over rows and cells
Sometimes, you'd like to just iterate over all the rows in a sheet, or all the cells in a row. This is possible with a simple for loop.
Luckily, this is very easy. Row defines a CellIterator inner class to handle iterating over the cells (get one with a call to row.cellIterator()), and Sheet provides a rowIterator() method to give an iterator over all the rows. These implement the java.lang.Iterable interface to allow foreach loops.
Sheet sheet = wb.getSheetAt(0);
for (Row row : sheet) {
for (Cell cell : row) {
// Do something here
}
}
Iterate over cells, with control of missing / blank cells
In some cases, when iterating, you need full control over how missing or blank rows and cells are treated, and you need to ensure you visit every cell and not just those defined in the file. (The CellIterator will only return the cells defined in the file, which is largely those with values or stylings, but it depends on Excel).
In cases such as these, you should fetch the first and last column information for a row, then call getCell(int, MissingCellPolicy) to fetch the cell. Use a MissingCellPolicy to control how blank or null cells are handled.
// Decide which rows to process
int rowStart = Math.min(15, sheet.getFirstRowNum());
int rowEnd = Math.max(1400, sheet.getLastRowNum());
for (int rowNum = rowStart; rowNum < rowEnd; rowNum++) {
Row r = sheet.getRow(rowNum);
int lastColumn = Math.max(r.getLastCellNum(), MY_MINIMUM_COLUMN_COUNT);
for (int cn = 0; cn < lastColumn; cn++) {
Cell c = r.getCell(cn, Row.RETURN_BLANK_AS_NULL);
if (c == null) {
// The spreadsheet is empty in this cell
} else {
// Do something useful with the cell's contents
}
}
}
Getting the cell contents
To get the contents of a cell, you first need to know what kind of cell it is (asking a string cell for its numeric contents will get you a NumberFormatException for example). So, you will want to switch on the cell's type, and then call the appropriate getter for that cell.
In the code below, we loop over every cell in one sheet, print out the cell's reference (eg A3), and then the cell's contents.
// import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.*;
Sheet sheet1 = wb.getSheetAt(0);
for (Row row : sheet1) {
for (Cell cell : row) {
CellReference cellRef = new CellReference(row.getRowNum(), cell.getColumnIndex());
System.out.print(cellRef.formatAsString());
System.out.print(" - ");
switch (cell.getCellType()) {
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_STRING:
System.out.println(cell.getRichStringCellValue().getString());
break;
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_NUMERIC:
if (DateUtil.isCellDateFormatted(cell)) {
System.out.println(cell.getDateCellValue());
} else {
System.out.println(cell.getNumericCellValue());
}
break;
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_BOOLEAN:
System.out.println(cell.getBooleanCellValue());
break;
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_FORMULA:
System.out.println(cell.getCellFormula());
break;
default:
System.out.println();
}
}
}
Text Extraction
For most text extraction requirements, the standard ExcelExtractor class should provide all you need.
InputStream inp = new FileInputStream("workbook.xls");
HSSFWorkbook wb = new HSSFWorkbook(new POIFSFileSystem(inp));
ExcelExtractor extractor = new ExcelExtractor(wb);
extractor.setFormulasNotResults(true);
extractor.setIncludeSheetNames(false);
String text = extractor.getText();
For very fancy text extraction, XLS to CSV etc, take a look at /src/examples/src/org/apache/poi/hssf/eventusermodel/examples/XLS2CSVmra.java
Fills and colors
Workbook wb = new XSSFWorkbook();
Sheet sheet = wb.createSheet("new sheet");
// Create a row and put some cells in it. Rows are 0 based.
Row row = sheet.createRow((short) 1);
// Aqua background
CellStyle style = wb.createCellStyle();
style.setFillBackgroundColor(IndexedColors.AQUA.getIndex());
style.setFillPattern(CellStyle.BIG_SPOTS);
Cell cell = row.createCell((short) 1);
cell.setCellValue("X");
cell.setCellStyle(style);
// Orange "foreground", foreground being the fill foreground not the font color.
style = wb.createCellStyle();
style.setFillForegroundColor(IndexedColors.ORANGE.getIndex());
style.setFillPattern(CellStyle.SOLID_FOREGROUND);
cell = row.createCell((short) 2);
cell.setCellValue("X");
cell.setCellStyle(style);
// Write the output to a file
FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream("workbook.xls");
wb.write(fileOut);
fileOut.close();
Merging cells
Workbook wb = new HSSFWorkbook();
Sheet sheet = wb.createSheet("new sheet");
Row row = sheet.createRow((short) 1);
Cell cell = row.createCell((short) 1);
cell.setCellValue("This is a test of merging");
sheet.addMergedRegion(new CellRangeAddress(
1, //first row (0-based)
1, //last row (0-based)
1, //first column (0-based)
2 //last column (0-based)
));
// Write the output to a file
FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream("workbook.xls");
wb.write(fileOut);
fileOut.close();
Working with fonts
Workbook wb = new HSSFWorkbook();
Sheet sheet = wb.createSheet("new sheet");
// Create a row and put some cells in it. Rows are 0 based.
Row row = sheet.createRow(1);
// Create a new font and alter it.
Font font = wb.createFont();
font.setFontHeightInPoints((short)24);
font.setFontName("Courier New");
font.setItalic(true);
font.setStrikeout(true);
// Fonts are set into a style so create a new one to use.
CellStyle style = wb.createCellStyle();
style.setFont(font);
// Create a cell and put a value in it.
Cell cell = row.createCell(1);
cell.setCellValue("This is a test of fonts");
cell.setCellStyle(style);
// Write the output to a file
FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream("workbook.xls");
wb.write(fileOut);
fileOut.close();
Note, the maximum number of unique fonts in a workbook is limited to 32767 ( the maximum positive short). You should re-use fonts in your apllications instead of creating a font for each cell. Examples:
Wrong:
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
Row row = sheet.createRow(i);
Cell cell = row.createCell((short) 0);
CellStyle style = workbook.createCellStyle();
Font font = workbook.createFont();
font.setBoldweight(Font.BOLDWEIGHT_BOLD);
style.setFont(font);
cell.setCellStyle(style);
}
Correct:
CellStyle style = workbook.createCellStyle();
Font font = workbook.createFont();
font.setBoldweight(Font.BOLDWEIGHT_BOLD);
style.setFont(font);
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
Row row = sheet.createRow(i);
Cell cell = row.createCell((short) 0);
cell.setCellStyle(style);
}
Custom colors
HSSF:
HSSFWorkbook wb = new HSSFWorkbook();
HSSFSheet sheet = wb.createSheet();
HSSFRow row = sheet.createRow((short) 0);
HSSFCell cell = row.createCell((short) 0);
cell.setCellValue("Default Palette");
//apply some colors from the standard palette,
// as in the previous examples.
//we'll use red text on a lime background
HSSFCellStyle style = wb.createCellStyle();
style.setFillForegroundColor(HSSFColor.LIME.index);
style.setFillPattern(HSSFCellStyle.SOLID_FOREGROUND);
HSSFFont font = wb.createFont();
font.setColor(HSSFColor.RED.index);
style.setFont(font);
cell.setCellStyle(style);
//save with the default palette
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("default_palette.xls");
wb.write(out);
out.close();
//now, let's replace RED and LIME in the palette
// with a more attractive combination
// (lovingly borrowed from freebsd.org)
cell.setCellValue("Modified Palette");
//creating a custom palette for the workbook
HSSFPalette palette = wb.getCustomPalette();
//replacing the standard red with freebsd.org red
palette.setColorAtIndex(HSSFColor.RED.index,
(byte) 153, //RGB red (0-255)
(byte) 0, //RGB green
(byte) 0 //RGB blue
);
//replacing lime with freebsd.org gold
palette.setColorAtIndex(HSSFColor.LIME.index, (byte) 255, (byte) 204, (byte) 102);
//save with the modified palette
// note that wherever we have previously used RED or LIME, the
// new colors magically appear
out = new FileOutputStream("modified_palette.xls");
wb.write(out);
out.close();
XSSF:
XSSFWorkbook wb = new XSSFWorkbook();
XSSFSheet sheet = wb.createSheet();
XSSFRow row = sheet.createRow(0);
XSSFCell cell = row.createCell( 0);
cell.setCellValue("custom XSSF colors");
XSSFCellStyle style1 = wb.createCellStyle();
style1.setFillForegroundColor(new XSSFColor(new java.awt.Color(128, 0, 128)));
style1.setFillPattern(CellStyle.SOLID_FOREGROUND);
Reading and Rewriting Workbooks
InputStream inp = new FileInputStream("workbook.xls");
//InputStream inp = new FileInputStream("workbook.xlsx");
Workbook wb = WorkbookFactory.create(inp);
Sheet sheet = wb.getSheetAt(0);
Row row = sheet.getRow(2);
Cell cell = row.getCell(3);
if (cell == null)
cell = row.createCell(3);
cell.setCellType(Cell.CELL_TYPE_STRING);
cell.setCellValue("a test");
// Write the output to a file
FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream("workbook.xls");
wb.write(fileOut);
fileOut.close();
Using newlines in cells
Workbook wb = new XSSFWorkbook(); //or new HSSFWorkbook();
Sheet sheet = wb.createSheet();
Row row = sheet.createRow(2);
Cell cell = row.createCell(2);
cell.setCellValue("Use \n with word wrap on to create a new line");
//to enable newlines you need set a cell styles with wrap=true
CellStyle cs = wb.createCellStyle();
cs.setWrapText(true);
cell.setCellStyle(cs);
//increase row height to accomodate two lines of text
row.setHeightInPoints((2*sheet.getDefaultRowHeightInPoints()));
//adjust column width to fit the content
sheet.autoSizeColumn((short)2);
FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream("ooxml-newlines.xlsx");
wb.write(fileOut);
fileOut.close();
Data Formats
Workbook wb = new HSSFWorkbook();
Sheet sheet = wb.createSheet("format sheet");
CellStyle style;
DataFormat format = wb.createDataFormat();
Row row;
Cell cell;
short rowNum = 0;
short colNum = 0;
row = sheet.createRow(rowNum++);
cell = row.createCell(colNum);
cell.setCellValue(11111.25);
style = wb.createCellStyle();
style.setDataFormat(format.getFormat("0.0"));
cell.setCellStyle(style);
row = sheet.createRow(rowNum++);
cell = row.createCell(colNum);
cell.setCellValue(11111.25);
style = wb.createCellStyle();
style.setDataFormat(format.getFormat("#,##0.0000"));
cell.setCellStyle(style);
FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream("workbook.xls");
wb.write(fileOut);
fileOut.close();
Fit Sheet to One Page
Workbook wb = new HSSFWorkbook();
Sheet sheet = wb.createSheet("format sheet");
PrintSetup ps = sheet.getPrintSetup();
sheet.setAutobreaks(true);
ps.setFitHeight((short)1);
ps.setFitWidth((short)1);
// Create various cells and rows for spreadsheet.
FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream("workbook.xls");
wb.write(fileOut);
fileOut.close();
Set Print Area
Workbook wb = new HSSFWorkbook();
Sheet sheet = wb.createSheet("Sheet1");
//sets the print area for the first sheet
wb.setPrintArea(0, "$A$1:$C$2");
//Alternatively:
wb.setPrintArea(
0, //sheet index
0, //start column
1, //end column
0, //start row
0 //end row
);
FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream("workbook.xls");
wb.write(fileOut);
fileOut.close();
Set Page Numbers on Footer
Workbook wb = new HSSFWorkbook(); // or new XSSFWorkbook();
Sheet sheet = wb.createSheet("format sheet");
Footer footer = sheet.getFooter();
footer.setRight( "Page " + HeaderFooter.page() + " of " + HeaderFooter.numPages() );
// Create various cells and rows for spreadsheet.
FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream("workbook.xls");
wb.write(fileOut);
fileOut.close();
Using the Convenience Functions
The convenience functions provide utility features such as setting borders around merged regions and changing style attributes without explicitly creating new styles.
Workbook wb = new HSSFWorkbook(); // or new XSSFWorkbook()
Sheet sheet1 = wb.createSheet( "new sheet" );
// Create a merged region
Row row = sheet1.createRow( 1 );
Row row2 = sheet1.createRow( 2 );
Cell cell = row.createCell( 1 );
cell.setCellValue( "This is a test of merging" );
CellRangeAddress region = CellRangeAddress.valueOf("B2:E5");
sheet1.addMergedRegion( region );
// Set the border and border colors.
final short borderMediumDashed = CellStyle.BORDER_MEDIUM_DASHED;
RegionUtil.setBorderBottom( borderMediumDashed,
region, sheet1, wb );
RegionUtil.setBorderTop( borderMediumDashed,
region, sheet1, wb );
RegionUtil.setBorderLeft( borderMediumDashed,
region, sheet1, wb );
RegionUtil.setBorderRight( borderMediumDashed,
region, sheet1, wb );
RegionUtil.setBottomBorderColor(IndexedColors.AQUA.getIndex(), region, sheet1, wb);
RegionUtil.setTopBorderColor(IndexedColors.AQUA.getIndex(), region, sheet1, wb);
RegionUtil.setLeftBorderColor(IndexedColors.AQUA.getIndex(), region, sheet1, wb);
RegionUtil.setRightBorderColor(IndexedColors.AQUA.getIndex(), region, sheet1, wb);
// Shows some usages of HSSFCellUtil
CellStyle style = wb.createCellStyle();
style.setIndention((short)4);
CellUtil.createCell(row, 8, "This is the value of the cell", style);
Cell cell2 = CellUtil.createCell( row2, 8, "This is the value of the cell");
CellUtil.setAlignment(cell2, wb, CellStyle.ALIGN_CENTER);
// Write out the workbook
FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream( "workbook.xls" );
wb.write( fileOut );
fileOut.close();
Shift rows up or down on a sheet
Workbook wb = new HSSFWorkbook();
Sheet sheet = wb.createSheet("row sheet");
// Create various cells and rows for spreadsheet.
// Shift rows 6 - 11 on the spreadsheet to the top (rows 0 - 5)
sheet.shiftRows(5, 10, -5);
Set a sheet as selected
Workbook wb = new HSSFWorkbook();
Sheet sheet = wb.createSheet("row sheet");
sheet.setSelected(true);
Set the zoom magnification
The zoom is expressed as a fraction. For example to express a zoom of 75% use 3 for the numerator and 4 for the denominator.
Workbook wb = new HSSFWorkbook();
Sheet sheet1 = wb.createSheet("new sheet");
sheet1.setZoom(3,4); // 75 percent magnification
Splits and freeze panes
There are two types of panes you can create; freeze panes and split panes.
A freeze pane is split by columns and rows. You create a freeze pane using the following mechanism:
sheet1.createFreezePane( 3, 2, 3, 2 );
The first two parameters are the columns and rows you wish to split by. The second two parameters indicate the cells that are visible in the bottom right quadrant.
Split pains appear differently. The split area is divided into four separate work area's. The split occurs at the pixel level and the user is able to adjust the split by dragging it to a new position.
Split panes are created with the following call:
sheet2.createSplitPane( 2000, 2000, 0, 0, Sheet.PANE_LOWER_LEFT );
The first parameter is the x position of the split. This is in 1/20th of a point. A point in this case seems to equate to a pixel. The second parameter is the y position of the split. Again in 1/20th of a point.
The last parameter indicates which pane currently has the focus. This will be one of Sheet.PANE_LOWER_LEFT, PANE_LOWER_RIGHT, PANE_UPPER_RIGHT or PANE_UPPER_LEFT.
Workbook wb = new HSSFWorkbook();
Sheet sheet1 = wb.createSheet("new sheet");
Sheet sheet2 = wb.createSheet("second sheet");
Sheet sheet3 = wb.createSheet("third sheet");
Sheet sheet4 = wb.createSheet("fourth sheet");
// Freeze just one row
sheet1.createFreezePane( 0, 1, 0, 1 );
// Freeze just one column
sheet2.createFreezePane( 1, 0, 1, 0 );
// Freeze the columns and rows (forget about scrolling position of the lower right quadrant).
sheet3.createFreezePane( 2, 2 );
// Create a split with the lower left side being the active quadrant
sheet4.createSplitPane( 2000, 2000, 0, 0, Sheet.PANE_LOWER_LEFT );
FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream("workbook.xls");
wb.write(fileOut);
fileOut.close();
Repeating rows and columns
It's possible to set up repeating rows and columns in your printouts by using the setRepeatingRows() and setRepeatingColumns() methods in the Sheet class.
These methods expect a CellRangeAddress parameter which specifies the range for the rows or columns to repeat. For setRepeatingRows(), it should specify a range of rows to repeat, with the column part spanning all columns. For setRepeatingColums(), it should specify a range of columns to repeat, with the row part spanning all rows. If the parameter is null, the repeating rows or columns will be removed.
Workbook wb = new HSSFWorkbook(); // or new XSSFWorkbook();
Sheet sheet1 = wb.createSheet("Sheet1");
Sheet sheet2 = wb.createSheet("Sheet2");
// Set the rows to repeat from row 4 to 5 on the first sheet.
sheet1.setRepeatingRows(CellRangeAddress.valueOf("4:5"));
// Set the columns to repeat from column A to C on the second sheet
sheet2.setRepeatingColumns(CellRangeAddress.valueOf("A:C"));
FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream("workbook.xls");
wb.write(fileOut);
fileOut.close();
Headers and Footers
Example is for headers but applies directly to footers.
Workbook wb = new HSSFWorkbook();
Sheet sheet = wb.createSheet("new sheet");
Header header = sheet.getHeader();
header.setCenter("Center Header");
header.setLeft("Left Header");
header.setRight(HSSFHeader.font("Stencil-Normal", "Italic") +
HSSFHeader.fontSize((short) 16) + "Right w/ Stencil-Normal Italic font and size 16");
FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream("workbook.xls");
wb.write(fileOut);
fileOut.close();
Drawing Shapes
POI supports drawing shapes using the Microsoft Office drawing tools. Shapes on a sheet are organized in a hiearchy of groups and and shapes. The top-most shape is the patriarch. This is not visisble on the sheet at all. To start drawing you need to call createPatriarch on the HSSFSheet class. This has the effect erasing any other shape information stored in that sheet. By default POI will leave shape records alone in the sheet unless you make a call to this method.
To create a shape you have to go through the following steps:
- Create the patriarch.
- Create an anchor to position the shape on the sheet.
- Ask the patriarch to create the shape.
- Set the shape type (line, oval, rectangle etc...)
- Set any other style details converning the shape. (eg: line thickness, etc...)
HSSFPatriarch patriarch = sheet.createDrawingPatriarch();
a = new HSSFClientAnchor( 0, 0, 1023, 255, (short) 1, 0, (short) 1, 0 );
HSSFSimpleShape shape1 = patriarch.createSimpleShape(a1);
shape1.setShapeType(HSSFSimpleShape.OBJECT_TYPE_LINE);
Text boxes are created using a different call:
HSSFTextbox textbox1 = patriarch.createTextbox(
new HSSFClientAnchor(0,0,0,0,(short)1,1,(short)2,2));
textbox1.setString(new HSSFRichTextString("This is a test") );
It's possible to use different fonts to style parts of the text in the textbox. Here's how:
HSSFFont font = wb.createFont();
font.setItalic(true);
font.setUnderline(HSSFFont.U_DOUBLE);
HSSFRichTextString string = new HSSFRichTextString("Woo!!!");
string.applyFont(2,5,font);
textbox.setString(string );
Just as can be done manually using Excel, it is possible to group shapes together. This is done by calling createGroup() and then creating the shapes using those groups.
It's also possible to create groups within groups.
Warning
Any group you create should contain at least two other shapes or subgroups.
Here's how to create a shape group:
// Create a shape group.
HSSFShapeGroup group = patriarch.createGroup(
new HSSFClientAnchor(0,0,900,200,(short)2,2,(short)2,2));
// Create a couple of lines in the group.
HSSFSimpleShape shape1 = group.createShape(new HSSFChildAnchor(3,3,500,500));
shape1.setShapeType(HSSFSimpleShape.OBJECT_TYPE_LINE);
( (HSSFChildAnchor) shape1.getAnchor() ).setAnchor((short)3,3,500,500);
HSSFSimpleShape shape2 = group.createShape(new HSSFChildAnchor((short)1,200,400,600));
shape2.setShapeType(HSSFSimpleShape.OBJECT_TYPE_LINE);
If you're being observant you'll noticed that the shapes that are added to the group use a new type of anchor: the HSSFChildAnchor. What happens is that the created group has it's own coordinate space for shapes that are placed into it. POI defaults this to (0,0,1023,255) but you are able to change it as desired. Here's how:
myGroup.setCoordinates(10,10,20,20); // top-left, bottom-right
If you create a group within a group it's also going to have it's own coordinate space.
Styling Shapes
By default shapes can look a little plain. It's possible to apply different styles to the shapes however. The sorts of things that can currently be done are:
- Change the fill color.
- Make a shape with no fill color.
- Change the thickness of the lines.
- Change the style of the lines. Eg: dashed, dotted.
- Change the line color.
Here's an examples of how this is done:
HSSFSimpleShape s = patriarch.createSimpleShape(a);
s.setShapeType(HSSFSimpleShape.OBJECT_TYPE_OVAL);
s.setLineStyleColor(10,10,10);
s.setFillColor(90,10,200);
s.setLineWidth(HSSFShape.LINEWIDTH_ONE_PT * 3);
s.setLineStyle(HSSFShape.LINESTYLE_DOTSYS);
Shapes and Graphics2d
While the native POI shape drawing commands are the recommended way to draw shapes in a shape it's sometimes desirable to use a standard API for compatibility with external libraries. With this in mind we created some wrappers for Graphics and Graphics2d.
Warning
It's important to not however before continuing that Graphics2d is a poor match to the capabilities of the Microsoft Office drawing commands. The olderGraphics class offers a closer match but is still a square peg in a round hole.
All Graphics commands are issued into an HSSFShapeGroup. Here's how it's done:
a = new HSSFClientAnchor( 0, 0, 1023, 255, (short) 1, 0, (short) 1, 0 );
group = patriarch.createGroup( a );
group.setCoordinates( 0, 0, 80 * 4 , 12 * 23 );
float verticalPointsPerPixel = a.getAnchorHeightInPoints(sheet) / (float)Math.abs(group.getY2() - group.getY1());
g = new EscherGraphics( group, wb, Color.black, verticalPointsPerPixel );
g2d = new EscherGraphics2d( g );
drawChemicalStructure( g2d );
The first thing we do is create the group and set it's coordinates to match what we plan to draw. Next we calculate a reasonable fontSizeMultipler then create the EscherGraphics object. Since what we really want is a Graphics2d object we create an EscherGraphics2d object and pass in the graphics object we created. Finally we call a routine that draws into the EscherGraphics2d object.
The vertical points per pixel deserves some more explanation. One of the difficulties in converting Graphics calls into escher drawing calls is that Excel does not have the concept of absolute pixel positions. It measures it's cell widths in 'characters' and the cell heights in points. Unfortunately it's not defined exactly what type of character it's measuring. Presumably this is due to the fact that the Excel will be using different fonts on different platforms or even within the same platform.
Because of this constraint we've had to implement the concept of a verticalPointsPerPixel. This the amount the font should be scaled by when you issue commands such as drawString(). To calculate this value use the follow formula:
multipler = groupHeightInPoints / heightOfGroup
The height of the group is calculated fairly simply by calculating the difference between the y coordinates of the bounding box of the shape. The height of the group can be calculated by using a convenience called HSSFClientAnchor.getAnchorHeightInPoints().
Many of the functions supported by the graphics classes are not complete. Here's some of the functions that are known to work.
- fillRect()
- fillOval()
- drawString()
- drawOval()
- drawLine()
- clearRect()
Functions that are not supported will return and log a message using the POI logging infrastructure (disabled by default).
Outlining
Outlines are great for grouping sections of information together and can be added easily to columns and rows using the POI API. Here's how:
Workbook wb = new HSSFWorkbook();
Sheet sheet1 = wb.createSheet("new sheet");
sheet1.groupRow( 5, 14 );
sheet1.groupRow( 7, 14 );
sheet1.groupRow( 16, 19 );
sheet1.groupColumn( (short)4, (short)7 );
sheet1.groupColumn( (short)9, (short)12 );
sheet1.groupColumn( (short)10, (short)11 );
FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream(filename);
wb.write(fileOut);
fileOut.close();
To collapse (or expand) an outline use the following calls:
sheet1.setRowGroupCollapsed( 7, true );
sheet1.setColumnGroupCollapsed( (short)4, true );
The row/column you choose should contain an already created group. It can be anywhere within the group.
Images
Images are part of the drawing support. To add an image just call createPicture() on the drawing patriarch. At the time of writing the following types are supported:
It should be noted that any existing drawings may be erased once you add a image to a sheet.
//create a new workbook
Workbook wb = new XSSFWorkbook(); //or new HSSFWorkbook();
//add picture data to this workbook.
InputStream is = new FileInputStream("image1.jpeg");
byte[] bytes = IOUtils.toByteArray(is);
int pictureIdx = wb.addPicture(bytes, Workbook.PICTURE_TYPE_JPEG);
is.close();
CreationHelper helper = wb.getCreationHelper();
//create sheet
Sheet sheet = wb.createSheet();
// Create the drawing patriarch. This is the top level container for all shapes.
Drawing drawing = sheet.createDrawingPatriarch();
//add a picture shape
ClientAnchor anchor = helper.createClientAnchor();
//set top-left corner of the picture,
//subsequent call of Picture#resize() will operate relative to it
anchor.setCol1(3);
anchor.setRow1(2);
Picture pict = drawing.createPicture(anchor, pictureIdx);
//auto-size picture relative to its top-left corner
pict.resize();
//save workbook
String file = "picture.xls";
if(wb instanceof XSSFWorkbook) file += "x";
FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream(file);
wb.write(fileOut);
fileOut.close();
Warning
Picture.resize() works only for JPEG and PNG. Other formats are not yet supported.
Reading images from a workbook:
List lst = workbook.getAllPictures();
for (Iterator it = lst.iterator(); it.hasNext(); ) {
PictureData pict = (PictureData)it.next();
String ext = pict.suggestFileExtension();
byte[] data = pict.getData();
if (ext.equals("jpeg")){
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("pict.jpg");
out.write(data);
out.close();
}
}
Named Ranges and Named Cells
Named Range is a way to refer to a group of cells by a name. Named Cell is a degenerate case of Named Range in that the 'group of cells' contains exactly one cell. You can create as well as refer to cells in a workbook by their named range. When working with Named Ranges, the classes: org.apache.poi.hssf.util.CellReference and & org.apache.poi.hssf.util.AreaReference are used (these work for both XSSF and HSSF, despite the package name).
Creating Named Range / Named Cell
// setup code
String sname = "TestSheet", cname = "TestName", cvalue = "TestVal";
Workbook wb = new HSSFWorkbook();
Sheet sheet = wb.createSheet(sname);
sheet.createRow(0).createCell((short) 0).setCellValue(cvalue);
// 1. create named range for a single cell using areareference
Name namedCell = wb.createName();
namedCell.setNameName(cname);
String reference = sname+"!A1:A1"; // area reference
namedCell.setRefersToFormula(reference);
// 2. create named range for a single cell using cellreference
Name namedCel2 = wb.createName();
namedCel2.setNameName(cname);
String reference = sname+"!A1"; // cell reference
namedCel2.setRefersToFormula(reference);
// 3. create named range for an area using AreaReference
Name namedCel3 = wb.createName();
namedCel3.setNameName(cname);
String reference = sname+"!A1:C5"; // area reference
namedCel3.setRefersToFormula(reference);
// 4. create named formula
Name namedCel4 = wb.createName();
namedCel4.setNameName("my_sum");
namedCel4.setRefersToFormula("SUM(sname+!$I$2:$I$6)");
Reading from Named Range / Named Cell
// setup code
String cname = "TestName";
Workbook wb = getMyWorkbook(); // retrieve workbook
// retrieve the named range
int namedCellIdx = wb.getNameIndex(cellName);
Name aNamedCell = wb.getNameAt(namedCellIdx);
// retrieve the cell at the named range and test its contents
AreaReference aref = new AreaReference(aNamedCell.getRefersToFormula());
CellReference[] crefs = aref.getAllReferencedCells();
for (int i=0; i<crefs.length; i++) {
Sheet s = wb.getSheet(crefs[i].getSheetName());
Row r = sheet.getRow(crefs[i].getRow());
Cell c = r.getCell(crefs[i].getCol());
// extract the cell contents based on cell type etc.
}
Reading from non-contiguous Named Ranges
// Setup code
String cname = "TestName";
Workbook wb = getMyWorkbook(); // retrieve workbook
// Retrieve the named range
// Will be something like "$C$10,$D$12:$D$14";
int namedCellIdx = wb.getNameIndex(cellName);
Name aNamedCell = wb.getNameAt(namedCellIdx);
// Retrieve the cell at the named range and test its contents
// Will get back one AreaReference for C10, and
// another for D12 to D14
AreaReference[] arefs = AreaReference.generateContiguous(aNamedCell.getRefersToFormula());
for (int i=0; i<arefs.length; i++) {
// Only get the corners of the Area
// (use arefs[i].getAllReferencedCells() to get all cells)
CellReference[] crefs = arefs[i].getCells();
for (int j=0; j<crefs.length; j++) {
// Check it turns into real stuff
Sheet s = wb.getSheet(crefs[j].getSheetName());
Row r = s.getRow(crefs[j].getRow());
Cell c = r.getCell(crefs[j].getCol());
// Do something with this corner cell
}
}
Note, when a cell is deleted, Excel does not delete the attached named range. As result, workbook can contain named ranges that point to cells that no longer exist. You should check the validity of a reference before constructing AreaReference
if(name.isDeleted()){
//named range points to a deleted cell.
} else {
AreaReference ref = new AreaReference(name.getRefersToFormula());
}
Cell Comments - HSSF and XSSF
A comment is a rich text note that is attached to & associated with a cell, separate from other cell content. Comment content is stored separate from the cell, and is displayed in a drawing object (like a text box) that is separate from, but associated with, a cell
Workbook wb = new XSSFWorkbook(); //or new HSSFWorkbook();
CreationHelper factory = wb.getCreationHelper();
Sheet sheet = wb.createSheet();
Row row = sheet.createRow(3);
Cell cell = row.createCell(5);
cell.setCellValue("F4");
Drawing drawing = sheet.createDrawingPatriarch();
// When the comment box is visible, have it show in a 1x3 space
ClientAnchor anchor = factory.createClientAnchor();
anchor.setCol1(cell.getColumnIndex());
anchor.setCol2(cell.getColumnIndex()+1);
anchor.setRow1(row.getRowNum());
anchor.setRow2(row.getRowNum()+3);
// Create the comment and set the text+author
Comment comment = drawing.createCellComment(anchor);
RichTextString str = factory.createRichTextString("Hello, World!");
comment.setString(str);
comment.setAuthor("Apache POI");
// Assign the comment to the cell
cell.setCellComment(comment);
String fname = "comment-xssf.xls";
if(wb instanceof XSSFWorkbook) fname += "x";
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(fname);
wb.write(out);
out.close();
Reading cell comments
Cell cell = sheet.get(3).getColumn((short)1);
Comment comment = cell.getCellComment();
if (comment != null) {
RichTextString str = comment.getString();
String author = comment.getAuthor();
}
// alternatively you can retrieve cell comments by (row, column)
comment = sheet.getCellComment(3, 1);
Adjust column width to fit the contents
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
sheet.autoSizeColumn(0); //adjust width of the first column
sheet.autoSizeColumn(1); //adjust width of the second column
Note, that Sheet#autoSizeColumn() does not evaluate formula cells, the width of formula cells is calculated based on the cached formula result. If your workbook has many formulas then it is a good idea to evaluate them before auto-sizing.
Warning
To calculate column width Sheet.autoSizeColumn uses Java2D classes that throw exception if graphical environment is not available. In case if graphical environment is not available, you must tell Java that you are running in headless mode and set the following system property: java.awt.headless=true . You should also ensure that the fonts you use in your workbook are available to Java.
How to read hyperlinks
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
Cell cell = sheet.getRow(0).getCell((short)0);
Hyperlink link = cell.getHyperlink();
if(link != null){
System.out.println(link.getAddress());
}
How to create hyperlinks
Workbook wb = new XSSFWorkbook(); //or new HSSFWorkbook();
CreationHelper createHelper = wb.getCreationHelper();
//cell style for hyperlinks
//by default hyperlinks are blue and underlined
CellStyle hlink_style = wb.createCellStyle();
Font hlink_font = wb.createFont();
hlink_font.setUnderline(Font.U_SINGLE);
hlink_font.setColor(IndexedColors.BLUE.getIndex());
hlink_style.setFont(hlink_font);
Cell cell;
Sheet sheet = wb.createSheet("Hyperlinks");
//URL
cell = sheet.createRow(0).createCell((short)0);
cell.setCellValue("URL Link");
Hyperlink link = createHelper.createHyperlink(Hyperlink.LINK_URL);
link.setAddress("http://poi.apache.org/");
cell.setHyperlink(link);
cell.setCellStyle(hlink_style);
//link to a file in the current directory
cell = sheet.createRow(1).createCell((short)0);
cell.setCellValue("File Link");
link = createHelper.createHyperlink(Hyperlink.LINK_FILE);
link.setAddress("link1.xls");
cell.setHyperlink(link);
cell.setCellStyle(hlink_style);
//e-mail link
cell = sheet.createRow(2).createCell((short)0);
cell.setCellValue("Email Link");
link = createHelper.createHyperlink(Hyperlink.LINK_EMAIL);
//note, if subject contains white spaces, make sure they are url-encoded
link.setAddress("mailto:poi@apache.org?subject=Hyperlinks");
cell.setHyperlink(link);
cell.setCellStyle(hlink_style);
//link to a place in this workbook
//create a target sheet and cell
Sheet sheet2 = wb.createSheet("Target Sheet");
sheet2.createRow(0).createCell((short)0).setCellValue("Target Cell");
cell = sheet.createRow(3).createCell((short)0);
cell.setCellValue("Worksheet Link");
Hyperlink link2 = createHelper.createHyperlink(Hyperlink.LINK_DOCUMENT);
link2.setAddress("'Target Sheet'!A1");
cell.setHyperlink(link2);
cell.setCellStyle(hlink_style);
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("hyperinks.xlsx");
wb.write(out);
out.close();
Data Validations
As of version 3.8, POI has slightly different syntax to work with data validations with .xls and .xlsx formats.
hssf.usermodel (binary .xls format)
Check the value a user enters into a cell against one or more predefined value(s).
The following code will limit the value the user can enter into cell A1 to one of three integer values, 10, 20 or 30.
HSSFWorkbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook();
HSSFSheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("Data Validation");
CellRangeAddressList addressList = new CellRangeAddressList(
0, 0, 0, 0);
DVConstraint dvConstraint = DVConstraint.createExplicitListConstraint(
new String[]{"10", "20", "30"});
DataValidation dataValidation = new HSSFDataValidation
(addressList, dvConstraint);
dataValidation.setSuppressDropDownArrow(true);
sheet.addValidationData(dataValidation);
Drop Down Lists:
This code will do the same but offer the user a drop down list to select a value from.
HSSFWorkbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook();
HSSFSheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("Data Validation");
CellRangeAddressList addressList = new CellRangeAddressList(
0, 0, 0, 0);
DVConstraint dvConstraint = DVConstraint.createExplicitListConstraint(
new String[]{"10", "20", "30"});
DataValidation dataValidation = new HSSFDataValidation
(addressList, dvConstraint);
dataValidation.setSuppressDropDownArrow(false);
sheet.addValidationData(dataValidation);
Messages On Error:
To create a message box that will be shown to the user if the value they enter is invalid.
dataValidation.setErrorStyle(DataValidation.ErrorStyle.STOP);
dataValidation.createErrorBox("Box Title", "Message Text");
Replace 'Box Title' with the text you wish to display in the message box's title bar and 'Message Text' with the text of your error message.
Prompts:
To create a prompt that the user will see when the cell containing the data validation receives focus
dataValidation.createPromptBox("Title", "Message Text");
dataValidation.setShowPromptBox(true);
The text encapsulated in the first parameter passed to the createPromptBox() method will appear emboldened and as a title to the prompt whilst the second will be displayed as the text of the message. The createExplicitListConstraint() method can be passed and array of String(s) containing interger, floating point, dates or text values.
Further Data Validations:
To obtain a validation that would check the value entered was, for example, an integer between 10 and 100, use the DVConstraint.createNumericConstraint(int, int, String, String) factory method.
dvConstraint = DVConstraint.createNumericConstraint(
DVConstraint.ValidationType.INTEGER,
DVConstraint.OperatorType.BETWEEN, "10", "100");
Look at the javadoc for the other validation and operator types; also note that not all validation types are supported for this method. The values passed to the two String parameters can be formulas; the '=' symbol is used to denote a formula
dvConstraint = DVConstraint.createNumericConstraint(
DVConstraint.ValidationType.INTEGER,
DVConstraint.OperatorType.BETWEEN, "=SUM(A1:A3)", "100");
It is not possible to create a drop down list if the createNumericConstraint() method is called, the setSuppressDropDownArrow(false) method call will simply be ignored.
Date and time constraints can be created by calling the createDateConstraint(int, String, String, String) or the createTimeConstraint(int, String, String). Both are very similar to the above and are explained in the javadoc.
Creating Data Validations From Spreadsheet Cells.
The contents of specific cells can be used to provide the values for the data validation and the DVConstraint.createFormulaListConstraint(String) method supports this. To specify that the values come from a contiguous range of cells do either of the following:
dvConstraint = DVConstraint.createFormulaListConstraint("$A$1:$A$3");
or
Name namedRange = workbook.createName();
namedRange.setNameName("list1");
namedRange.setRefersToFormula("$A$1:$A$3");
dvConstraint = DVConstraint.createFormulaListConstraint("list1");
and in both cases the user will be able to select from a drop down list containing the values from cells A1, A2 and A3.
The data does not have to be as the data validation. To select the data from a different sheet however, the sheet must be given a name when created and that name should be used in the formula. So assuming the existence of a sheet named 'Data Sheet' this will work:
Name namedRange = workbook.createName();
namedRange.setNameName("list1");
namedRange.setRefersToFormula("'Data Sheet'!$A$1:$A$3");
dvConstraint = DVConstraint.createFormulaListConstraint("list1");
as will this:
dvConstraint = DVConstraint.createFormulaListConstraint("'Data Sheet'!$A$1:$A$3");
whilst this will not:
Name namedRange = workbook.createName();
namedRange.setNameName("list1");
namedRange.setRefersToFormula("'Sheet1'!$A$1:$A$3");
dvConstraint = DVConstraint.createFormulaListConstraint("list1");
and nor will this:
dvConstraint = DVConstraint.createFormulaListConstraint("'Sheet1'!$A$1:$A$3");
xssf.usermodel (.xlsx format)
Data validations work similarly when you are creating an xml based, SpreadsheetML, workbook file; but there are differences. Explicit casts are required, for example, in a few places as much of the support for data validations in the xssf stream was built into the unifying ss stream, of which more later. Other differences are noted with comments in the code.
Check the value the user enters into a cell against one or more predefined value(s).
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
XSSFSheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("Data Validation");
XSSFDataValidationHelper dvHelper = new XSSFDataValidationHelper(sheet);
XSSFDataValidationConstraint dvConstraint = (XSSFDataValidationConstraint)
dvHelper.createExplicitListConstraint(new String[]{"11", "21", "31"});
CellRangeAddressList addressList = new CellRangeAddressList(0, 0, 0, 0);
XSSFDataValidation validation =(XSSFDataValidation)dvHelper.createValidation(
dvConstraint, addressList);
// Here the boolean value false is passed to the setSuppressDropDownArrow()
// method. In the hssf.usermodel examples above, the value passed to this
// method is true.
validation.setSuppressDropDownArrow(false);
// Note this extra method call. If this method call is omitted, or if the
// boolean value false is passed, then Excel will not validate the value the
// user enters into the cell.
validation.setShowErrorBox(true);
sheet.addValidationData(validation);
Drop Down Lists:
This code will do the same but offer the user a drop down list to select a value from.
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
XSSFSheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("Data Validation");
XSSFDataValidationHelper dvHelper = new XSSFDataValidationHelper(sheet);
XSSFDataValidationConstraint dvConstraint = (XSSFDataValidationConstraint)
dvHelper.createExplicitListConstraint(new String[]{"11", "21", "31"});
CellRangeAddressList addressList = new CellRangeAddressList(0, 0, 0, 0);
XSSFDataValidation validation = (XSSFDataValidation)dvHelper.createValidation(
dvConstraint, addressList);
validation.setShowErrorBox(true);
sheet.addValidationData(validation);
Note that the call to the setSuppressDropDowmArrow() method can either be simply excluded or replaced with:
validation.setSuppressDropDownArrow(true);
Prompts and Error Messages:
These both exactly mirror the hssf.usermodel so please refer to the 'Messages On Error:' and 'Prompts:' sections above.
Further Data Validations:
To obtain a validation that would check the value entered was, for example, an integer between 10 and 100, use the XSSFDataValidationHelper(s) createNumericConstraint(int, int, String, String) factory method.
XSSFDataValidationConstraint dvConstraint = (XSSFDataValidationConstraint)
dvHelper.createNumericConstraint(
XSSFDataValidationConstraint.ValidationType.INTEGER,
XSSFDataValidationConstraint.OperatorType.BETWEEN,
"10", "100");
The values passed to the final two String parameters can be formulas; the '=' symbol is used to denote a formula. Thus, the following would create a validation the allows values only if they fall between the results of summing two cell ranges
XSSFDataValidationConstraint dvConstraint = (XSSFDataValidationConstraint)
dvHelper.createNumericConstraint(
XSSFDataValidationConstraint.ValidationType.INTEGER,
XSSFDataValidationConstraint.OperatorType.BETWEEN,
"=SUM(A1:A10)", "=SUM(B24:B27)");
It is not possible to create a drop down list if the createNumericConstraint() method is called, the setSuppressDropDownArrow(true) method call will simply be ignored.
Please check the javadoc for other constraint types as examples for those will not be included here. There are, for example, methods defined on the XSSFDataValidationHelper class allowing you to create the following types of constraint; date, time, decimal, integer, numeric, formula, text length and custom constraints.
Creating Data Validations From Spread Sheet Cells:
One other type of constraint not mentioned above is the formula list constraint. It allows you to create a validation that takes it value(s) from a range of cells. This code
XSSFDataValidationConstraint dvConstraint = (XSSFDataValidationConstraint)
dvHelper.createFormulaListConstraint("$A$1:$F$1");
would create a validation that took it's values from cells in the range A1 to F1.
The usefulness of this technique can be extended if you use named ranges like this;
XSSFName name = workbook.createName();
name.setNameName("data");
name.setRefersToFormula("$B$1:$F$1");
XSSFDataValidationHelper dvHelper = new XSSFDataValidationHelper(sheet);
XSSFDataValidationConstraint dvConstraint = (XSSFDataValidationConstraint)
dvHelper.createFormulaListConstraint("data");
CellRangeAddressList addressList = new CellRangeAddressList(
0, 0, 0, 0);
XSSFDataValidation validation = (XSSFDataValidation)
dvHelper.createValidation(dvConstraint, addressList);
validation.setSuppressDropDownArrow(true);
validation.setShowErrorBox(true);
sheet.addValidationData(validation);
OpenOffice Calc has slightly different rules with regard to the scope of names. Excel supports both Workbook and Sheet scope for a name but Calc does not, it seems only to support Sheet scope for a name. Thus it is often best to fully qualify the name for the region or area something like this;
XSSFName name = workbook.createName();
name.setNameName("data");
name.setRefersToFormula("'Data Validation'!$B$1:$F$1");
....
This does open a further, interesting opportunity however and that is to place all of the data for the validation(s) into named ranges of cells on a hidden sheet within the workbook. These ranges can then be explicitly identified in the setRefersToFormula() method argument.
ss.usermodel
The classes within the ss.usermodel package allow developers to create code that can be used to generate both binary (.xls) and SpreadsheetML (.xlsx) workbooks.
The techniques used to create data validations share much in common with the xssf.usermodel examples above. As a result just one or two examples will be presented here.
Check the value the user enters into a cell against one or more predefined value(s).
Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(); // or new HSSFWorkbook
Sheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("Data Validation");
DataValidationHelper dvHelper = sheet.getDataValidationHelper();
DataValidationConstraint dvConstraint = dvHelper.createExplicitListConstraint(
new String[]{"13", "23", "33"});
CellRangeAddressList addressList = new CellRangeAddressList(0, 0, 0, 0);
DataValidation validation = dvHelper.createValidation(
dvConstraint, addressList);
// Note the check on the actual type of the DataValidation object.
// If it is an instance of the XSSFDataValidation class then the
// boolean value 'false' must be passed to the setSuppressDropDownArrow()
// method and an explicit call made to the setShowErrorBox() method.
if(validation instanceof XSSFDataValidation) {
validation.setSuppressDropDownArrow(false);
validation.setShowErrorBox(true);
}
else {
// If the Datavalidation contains an instance of the HSSFDataValidation
// class then 'true' should be passed to the setSuppressDropDownArrow()
// method and the call to setShowErrorBox() is not necessary.
validation.setSuppressDropDownArrow(true);
}
sheet.addValidationData(validation);
Drop Down Lists:
This code will do the same but offer the user a drop down list to select a value from.
Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(); // or new HSSFWorkbook
Sheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("Data Validation");
DataValidationHelper dvHelper = sheet.getDataValidationHelper();
DataValidationConstraint dvConstraint = dvHelper.createExplicitListConstraint(
new String[]{"13", "23", "33"});
CellRangeAddressList addressList = new CellRangeAddressList(0, 0, 0, 0);
DataValidation validation = dvHelper.createValidation(
dvConstraint, addressList);
// Note the check on the actual type of the DataValidation object.
// If it is an instance of the XSSFDataValidation class then the
// boolean value 'false' must be passed to the setSuppressDropDownArrow()
// method and an explicit call made to the setShowErrorBox() method.
if(validation instanceof XSSFDataValidation) {
validation.setSuppressDropDownArrow(true);
validation.setShowErrorBox(true);
}
else {
// If the Datavalidation contains an instance of the HSSFDataValidation
// class then 'true' should be passed to the setSuppressDropDownArrow()
// method and the call to setShowErrorBox() is not necessary.
validation.setSuppressDropDownArrow(false);
}
sheet.addValidationData(validation);
Prompts and Error Messages:
These both exactly mirror the hssf.usermodel so please refer to the 'Messages On Error:' and 'Prompts:' sections above.
As the differences between the ss.usermodel and xssf.usermodel examples are small - restricted largely to the way the DataValidationHelper is obtained, the lack of any need to explicitly cast data types and the small difference in behaviour between the hssf and xssf interpretation of the setSuppressDropDowmArrow() method, no further examples will be included in this section.
Advanced Data Validations.
Dependent Drop Down Lists.
In some cases, it may be necessary to present to the user a sheet which contains more than one drop down list. Further, the choice the user makes in one drop down list may affect the options that are presented to them in the second or subsequent drop down lists. One technique that may be used to implement this behaviour will now be explained.
There are two keys to the technique; one is to use named areas or regions of cells to hold the data for the drop down lists, the second is to use the INDIRECT() function to convert between the name and the actual addresses of the cells. In the example section there is a complete working example- called LinkedDropDownLists.java - that demonstrates how to create linked or dependent drop down lists. Only the more relevant points are explained here.
To create two drop down lists where the options shown in the second depend upon the selection made in the first, begin by creating a named region of cells to hold all of the data for populating the first drop down list. Next, create a data validation that will look to this named area for its data, something like this;
CellRangeAddressList addressList = new CellRangeAddressList(0, 0, 0, 0);
DataValidationHelper dvHelper = sheet.getDataValidationHelper();
DataValidationConstraint dvConstraint = dvHelper.createFormulaListConstraint(
"CHOICES");
DataValidation validation = dvHelper.createValidation(
dvConstraint, addressList);
sheet.addValidationData(validation);
Note that the name of the area - in the example above it is 'CHOICES' - is simply passed to the createFormulaListConstraint() method. This is sufficient to cause Excel to populate the drop down list with data from that named region.
Next, for each of the options the user could select in the first drop down list, create a matching named region of cells. The name of that region should match the text the user could select in the first drop down list. Note, in the example, all upper case letters are used in the names of the regions of cells.
Now, very similar code can be used to create a second, linked, drop down list;
CellRangeAddressList addressList = new CellRangeAddressList(0, 0, 1, 1);
DataValidationConstraint dvConstraint = dvHelper.createFormulaListConstraint(
"INDIRECT(UPPER($A$1))");
DataValidation validation = dvHelper.createValidation(
dvConstraint, addressList);
sheet.addValidationData(validation);
The key here is in the following Excel function - INDIRECT(UPPER($A$1)) - which is used to populate the second, linked, drop down list. Working from the inner-most pair of brackets, it instructs Excel to look at the contents of cell A1, to convert what it reads there into upper case – as upper case letters are used in the names of each region - and then convert this name into the addresses of those cells that contain the data to populate another drop down list.
Embedded Objects
It is possible to perform more detailed processing of an embedded Excel, Word or PowerPoint document, or to work with any other type of embedded object.
HSSF:
POIFSFileSystem fs = new POIFSFileSystem(new FileInputStream("excel_with_embeded.xls"));
HSSFWorkbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(fs);
for (HSSFObjectData obj : workbook.getAllEmbeddedObjects()) {
//the OLE2 Class Name of the object
String oleName = obj.getOLE2ClassName();
if (oleName.equals("Worksheet")) {
DirectoryNode dn = (DirectoryNode) obj.getDirectory();
HSSFWorkbook embeddedWorkbook = new HSSFWorkbook(dn, fs, false);
//System.out.println(entry.getName() + ": " + embeddedWorkbook.getNumberOfSheets());
} else if (oleName.equals("Document")) {
DirectoryNode dn = (DirectoryNode) obj.getDirectory();
HWPFDocument embeddedWordDocument = new HWPFDocument(dn, fs);
//System.out.println(entry.getName() + ": " + embeddedWordDocument.getRange().text());
} else if (oleName.equals("Presentation")) {
DirectoryNode dn = (DirectoryNode) obj.getDirectory();
SlideShow embeddedPowerPointDocument = new SlideShow(new HSLFSlideShow(dn, fs));
//System.out.println(entry.getName() + ": " + embeddedPowerPointDocument.getSlides().length);
} else {
if(obj.hasDirectoryEntry()){
// The DirectoryEntry is a DocumentNode. Examine its entries to find out what it is
DirectoryNode dn = (DirectoryNode) obj.getDirectory();
for (Iterator entries = dn.getEntries(); entries.hasNext();) {
Entry entry = (Entry) entries.next();
//System.out.println(oleName + "." + entry.getName());
}
} else {
// There is no DirectoryEntry
// Recover the object's data from the HSSFObjectData instance.
byte[] objectData = obj.getObjectData();
}
}
}
XSSF:
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook("excel_with_embeded.xlsx");
for (PackagePart pPart : workbook.getAllEmbedds()) {
String contentType = pPart.getContentType();
// Excel Workbook - either binary or OpenXML
if (contentType.equals("application/vnd.ms-excel")) {
HSSFWorkbook embeddedWorkbook = new HSSFWorkbook(pPart.getInputStream());
}
// Excel Workbook - OpenXML file format
else if (contentType.equals("application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheet")) {
OPCPackage docPackage = OPCPackage.open(pPart.getInputStream());
XSSFWorkbook embeddedWorkbook = new XSSFWorkbook(docPackage);
}
// Word Document - binary (OLE2CDF) file format
else if (contentType.equals("application/msword")) {
HWPFDocument document = new HWPFDocument(pPart.getInputStream());
}
// Word Document - OpenXML file format
else if (contentType.equals("application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document")) {
OPCPackage docPackage = OPCPackage.open(pPart.getInputStream());
XWPFDocument document = new XWPFDocument(docPackage);
}
// PowerPoint Document - binary file format
else if (contentType.equals("application/vnd.ms-powerpoint")) {
HSLFSlideShow slideShow = new HSLFSlideShow(pPart.getInputStream());
}
// PowerPoint Document - OpenXML file format
else if (contentType.equals("application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.presentationml.presentation")) {
OPCPackage docPackage = OPCPackage.open(pPart.getInputStream());
XSLFSlideShow slideShow = new XSLFSlideShow(docPackage);
}
// Any other type of embedded object.
else {
System.out.println("Unknown Embedded Document: " + contentType);
InputStream inputStream = pPart.getInputStream();
}
}
(Since POI-3.7)
Autofilters
Workbook wb = new HSSFWorkbook(); //or new XSSFWorkbook();
Sheet sheet = wb.createSheet();
sheet.setAutoFilter(CellRangeAddress.valueOf("C5:F200"));
Conditional Formatting
Workbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(); // or new XSSFWorkbook();
Sheet sheet = workbook.createSheet();
SheetConditionalFormatting sheetCF = sheet.getSheetConditionalFormatting();
ConditionalFormattingRule rule1 = sheetCF.createConditionalFormattingRule(ComparisonOperator.EQUAL, "0");
FontFormatting fontFmt = rule1.createFontFormatting();
fontFmt.setFontStyle(true, false);
fontFmt.setFontColorIndex(IndexedColors.DARK_RED.index);
BorderFormatting bordFmt = rule1.createBorderFormatting();
bordFmt.setBorderBottom(BorderFormatting.BORDER_THIN);
bordFmt.setBorderTop(BorderFormatting.BORDER_THICK);
bordFmt.setBorderLeft(BorderFormatting.BORDER_DASHED);
bordFmt.setBorderRight(BorderFormatting.BORDER_DOTTED);
PatternFormatting patternFmt = rule1.createPatternFormatting();
patternFmt.setFillBackgroundColor(IndexedColors.YELLOW.index);
ConditionalFormattingRule rule2 = sheetCF.createConditionalFormattingRule(ComparisonOperator.BETWEEN, "-10", "10");
ConditionalFormattingRule [] cfRules =
{
rule1, rule2
};
CellRangeAddress[] regions = {
CellRangeAddress.valueOf("A3:A5")
};
sheetCF.addConditionalFormatting(regions, cfRules);
See more examples on Excel conditional formatting in ConditionalFormats.java
Hiding and Un-Hiding Rows
Using Excel, it is possible to hide a row on a worksheet by selecting that row (or rows), right clicking once on the right hand mouse button and selecting 'Hide' from the pop=up menu that appears.
To emulate this using POI, simply call the setZeroHeight() method on an instance of either XSSFRow or HSSFRow (the method is defined on the ss.usermodel.Row interface that both classes implement), like this:
Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(); // OR new HSSFWorkbook()
Sheet sheet = workbook.createSheet(0);
Row row = workbook.createRow(0);
row.setZeroHeight();
If the file were saved away to disc now, then the first row on the first sheet would not be visible.
Using Excel, it is possible to unhide previously hidden rows by selecting the row above and the row below the one that is hidden and then pressing and holding down the Ctrl key, the Shift and the pressing the number 9 before releasing them all.
To emulate this behaviour using POI do something like this:
Workbook workbook = WorkbookFactory.create(new File(.......));
Sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
Iterator<Row> row Iter = sheet.iterator();
while(rowIter.hasNext()) {
Row row = rowIter.next();
if(row.getZeroHeight()) {
row.setZeroHeight(false);
}
}
If the file were saved away to disc now, any previously hidden rows on the first sheet of the workbook would now be visible.
The example illustrates two features. Firstly, that it is possible to unhide a row simply by calling the setZeroHeight() method and passing the boolean value 'false'. Secondly, it ilustrates how to test whther a row is hidden or not. Simply call the getZeroHeight() method and it will return 'true' if the row is hidden, 'false' otherwise.

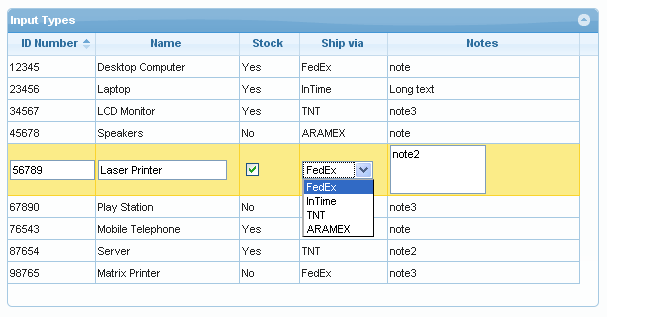

Discussion
Is it possible to have diff fields for form edit and inline edit in a same grid?
There is an escaping bug with special characters. Try insert <script>alert('hello')</script> into a field. It should be displayed as common text, but its executed. This is a common problem with inline editing.
Take a look at http://www.jstree.com/documentation/crrm (rename section)
Hi. I can't get editRow to eval the JSON in responseText. May there be an encoding issue? I've got something like
jQuery(”#tableId”).editRow(
rowId, true, null, function(xhr) { var data = eval(xhr.responseText); // nothing happens if(data.result == "success") { jQuery("#"+tableId).jqGrid('delRowData',rowId); } }, ajaxurl, postData);
Thanks
jQuery(”#tableId”).editRow( rowId, true, null, function(xhr) { var data = eval('(' + xhr.responseText + ')'); if(data.result == “success”) { jQuery(”#”+tableId).jqGrid('delRowData',rowId); } }, ajaxurl, postData );Regards. Santiago
How is it possible to edit inline the grid without sending the data to the server, like shown on the example “Edit Row” (on the demo web site of trirand.com). The reason is that I have no PHP server and I want to save the grid locally.
And my second question: I wanted to serialize the grid data in a XML string: is it included in this plugin ?
Thanks, Pascal
After reading more carefully this page (sorry was too lazy …), I 've found the solution to save inside the grid only:
⇒> jQuery(”#grid_id”).saveRow(“rowid”, false, 'clientArray');
Data will not be posted to server. I am happy !!!
I'm using the jqgrid 4 development, so i want to colaborate with that project.
I found a problem with inline editing. jqgrid 4 sets focus by static value. So i'm using onCellSelect and just added an extra param to editRow method. So i did edit grid.inlinedir.js, adding focus on the parameters and removing the variable declaration 'focus=null'.
I did send the iCol param of onCellSelect by the focus param to the editRow method.
That is my code:
var lastsel; $(function(){ jQuery(”#rowed6”).jqGrid({ url:“listJSON”, editurl:“updateJSON”, datatype: “json”, height: 250, colNames:['Id','Data Inicial','Data final','Versão', 'Finalidade do Arquivo','codFin'], colModel:[ {name:'id',index:'id', width:90, sorttype:“int”}, {name:'dtIni',index:'dtIni',classes:'dtPicker',width:90,editable:true,sorttype:'date', editoptions:{ dataInit:function (elem) { $(elem).datepicker(); } }}, {name:'dtFin',index:'dtFin',classes:'dtPicker',width:90,editable:true,sorttype:'date', editoptions:{ dataInit:function (elem) { $(elem).datepicker(); } }}, {name:'codVer',index:'codVer',width:150,editable:true,editoptions:{size:“20”,maxlength:“30”}}, {name:'descCodVer',index:'descCodVer',width:150,editable:true,editoptions:{size:“20”,maxlength:“30”}}, {name:'codFin',index:'codFin',hidden: true} ], caption: “Date Picker Integration”, onCellSelect:function(rowid,iCol,cellcontent,e){ if(rowid && rowid!==lastsel){ jQuery('#rowed6').restoreRow(lastsel); lastsel=rowid; } jQuery('#rowed6').editRow(rowid, true,iCol); }, autowidth:true, rowNum:10, rowList:[10,20,30], pager: '#prowed3', sortname: 'id', viewrecords: true, sortorder: “asc” }); jQuery(”#rowed6”).jqGrid('navGrid',”#prowed3”,{edit:false,add:false,del:false}); });grid.inlinedir.js line 13 -
editRow : function(rowid,keys,focus,oneditfunc,succesfunc, url, extraparam, aftersavefunc,errorfunc, afterrestorefunc)line 35 -
var $t = this, nm, tmp, editable, cnt=0, svr={}, ind,cm;It could be great if the data being edited do not change, then the data won't be saved to the server (that is the expected behaviour, I think ;) ).
Currently there is any way to do this?
There is a primitive solution to sort this problem at: http://stackoverflow.com/questions/6360512/jqgrid-inline-edit-detect-dirty-changed-cells/7141667
I'm a long-time fan of jqGrid and I hate to make my first official contact on the website a technical issue but this one has me really stumped (and I have rummaged through the documentation and searched all over the internets) …
I am using a jqGrid (latest version) in inline-edit mode to manage data completely on the client side (dataType is 'local'; I upload it to the server once the user is ready to move to the next phase). I use a OnSelectRow event to save the row being edited when you click on a different row. Both the editRow and saveRow methods in the event handler make a reference to 'clientArray'. editRow also uses keys = true (so I expect it to act accordingly on the Esc and Enter keys).
I am seeing this buggy behavior where pressing Enter only makes it “appear” that the data has been saved. The data in the underlying array (getGridParam('data')) is still unchanged. The only way data gets truly saved is when I click to a different row (and the OnSelectRow handler takes care of saving the row explicitly). Pressing Enter with keys = true (according to the source code) calls saveRow with rowId and “o” which appears to be the settings array starting with “keys”. Well, that would yield very different results given the saveRow method signature starts with “successfunc”. I have a feeling that this is causing the Enter-based saveRow to behave quite differently from the explicit saveRow in OnSelectRow because the parameter 'clientArray' is misaligned and the saveRow method treats it as some other sort of storage location (server-, url-based?). Any thoughts?
Thank you, all, in advance.
Tengo un problema con el dataInit reulta que deseo mostrar el formulario de editar y tengo dos campos fecha y quiero a ambos asignar el “datepicker”; lo asigna corectamente a ambos pero cuando deseo cambiar la fecha del segundo campo se pasa el foco al primer campo: Les dejo mi codigo…
jQuery(”#listado_es”).jqGrid({
height: 200, url:'reges_detalle.php?q=1', datatype: "xml", colNames:['Fecha inicio','Fecha fin', 'Tipo', 'estado'], colModel:[ {name:'horaent',index:'horaent',width:130,editable:true,searchtype:"date", sorttype:"datetime", formatter:'datetime', editrules:{custom:true, custom_func:valfechahora}, searchoptions:{dataInit:function(elb){$(elb).datepicker({dateFormat:'yy-mm-dd'});} }, editoptions:{ size:25, /* dataInit:function(horaent){ $(horaent).datepicker(); }*/ }}, {name:'horasal',index:'horasal',width:130,editable:true,searchtype:"date", sorttype:"datetime", formatter:'datetime', editrules:{custom:true, custom_func:valfechahora}, searchoptions:{ dataInit:function(elex){ $(elex).datepicker({dateFormat:'yy-mm-dd'}); } }, editoptions:{ size:25, /* dataInit:function(horasal){ $(horasal).datepicker(); }*/ }}, {name:'nom_dep',index:'nom_dep', width:200,editable:true,edittype:"select", editoptions:{ dataUrl:'includes/cargar_selec_normal.php'+parametros, }}, {name:'pta_ent',index:'pta_ent', width:200}, ], rowNum:10, rowList:[5,10,20], pager: '#pager_es', sortname: 'horaent', viewrecords: true, sortorder: "asc", editurl:'opera.php', caption:"--------------" }) jQuery("#listado_es").jqGrid('navGrid','#pager_es',{add:false,edit:false,del:false}, {}, {}, {}, {multipleSearch:true});Espero me puedan ayudar a solucionar este problema
Is there an easy way to check if the row is open for editing before acting on the key events. Currently I'm looping through RowIDs and comparing them and if it's the same then I save it.
Hi, i've found a small bug into the createEl function of grid.common.js (i use the 3.8.2 version but i see that is present in the 4.3.1 too). If i set a dataUrl for create a select element within inline editing, if the value (or text) of options contains html entity, in my case blank space ( ), when i click on row and go in edit mode the selected element not correspond with the option with the same text.
This occurs because this code checks for the text() or val() of an option into the value (ovm) (or values if multiselect) :
setTimeout(function(){ $(“option”,elem).each(function(i){ if(i===0) { this.selected = ””; } $(this).attr(“role”,”option”); if($.inArray($.trim($(this).text()),ovm) > -1 || $.inArray($.trim($(this).val()),ovm) > -1 ) { this.selected= “selected”; if(!msl) { return false; } } }); },0);I solved adding the checks for the html() …so:Hope this help, Bye Gabriele
Haz lo siguiente:
Dentro de la funcion dataInit $(elemento_select).trigger('change') algo asi:
editoptions:{
size:25, dataInit:function(ele){ $(ele).trigger('change') }}
I am having an issue with getting the keys (Esc and Enter) to work on a new record. Below is the code for my button:
$(”#t_clients”).append('<button type=“button” onclick=“$(\'#clients\').jqGrid(\'addRow\', {addRowParams: {extraparam: {keys: true}} });”>Add Client</button>');According to the documentation, it seems like this should be working. Unfortunately, it doesn't. Any help would be greatly appreciated.
when using actions formatter (http://www.trirand.com/jqgridwiki/doku.php?id=wiki:predefined_formatter) restore rows like this
if(id && id!==lastsel2){ jQuery.fn.fmatter.rowactions(lastsel2,'rowed5','cancel',0); jQuery('#rowed5').editRow(id,true); lastsel2=id; }instead of
if(id && id!==lastsel2){ jQuery('#rowed5').restoreRow(lastsel2); jQuery('#rowed5').editRow(id,true); lastsel2=id; }It is more complete, not only restore row but restore edit buttons also. you can call the function using the onEdit event on colmodel.
;)
put formatter:'select' in select columns to get the value instead of text of the line