<jQuery Core>
1. jQuery( html ) Returns: jQuery
jQuery( html ), 실행후 jQuery객체를 반환
Create DOM elements on-the-fly from the provided String of raw HTML.
주어진 html을 가지고 빠르게 문서 원소를 생성한다.
그리고 jQuery객체로서 그 것을 반환한다.
이말은 그것을 이어서 jQuery의 다른 함수와 함께 사용가능하다는 뜻이다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("<div><p>Hello</p></div>").appendTo("body");
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
2. jQuery( elements ) Returns: jQuery
jQuery( 원소 ) jQuery( 원소.원소.원소 ), 실행후 jQuery객체를 반환
Wrap jQuery functionality around a single or multiple DOM Element(s).
하나 또는 다단계의 문서원소로서 사용할수 있다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$(document.body).css( "background", "black" );
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
3. jQuery( callback ) Returns: jQuery
jQuery( 콜백함수 ), 실행후 jQuery객체를 반환
A shorthand for $(document).ready().
$()은 $(document).ready() 의 짧은 표현으로 사용가능하다.
$(document).ready() 은 문서가 사용가능한 시점을 자동으로 인식하여 주어진 콜백 함수를 동작시킨다.
콜백함수란 지정된 행위가 끝난다음 자동적으로 실행될 함수를 의미한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(function(){
$(document.body).css( "background", "black" );
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
4. each( callback ) Returns: jQuery
each( 콜백함수 ), 실행후 jQuery객체를 반환
Execute a function within the context of every matched element.
매치 되어진 모든 원소에 대해 주어진 콜백 함수를 실행한다. 루프의 의미이다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$(document.body).click(function () {
$("div").each(function (i) {
if (this.style.color != "blue") {
this.style.color = "blue";
} else {
this.style.color = "";
}
});
});
});
</script>
<style>
div { color:red; text-align:center; cursor:pointer;
font-weight:bolder; width:300px; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>Click here</div>
<div>to iterate through</div>
<div>these divs.</div>
</body>
</html>
5. size( ) Returns: Number
size( ), 실행후 숫자를 반환
The number of elements in the jQuery object.
매치되어진 원소들의 갯수를 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$(document.body).click(function () {
$(document.body).append($("<div>"));
var n = $("div").size();
$("span").text("There are " + n + " divs." +
"Click to add more.");
}).click(); // trigger the click to start
});
</script>
<style>
body { cursor:pointer; }
div { width:50px; height:30px; margin:5px; float:left;
background:blue; }
span { color:red; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<span></span>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
6. length Returns: Number
length, 실행후 숫자를 반환
The number of elements in the jQuery object.
매치되어진 원소들의 갯수를 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$(document.body).click(function () {
$(document.body).append($("<div>"));
var n = $("div").length;
$("span").text("There are " + n + " divs." +
"Click to add more.");
}).trigger('click'); // trigger the click to start
});
</script>
<style>
body { cursor:pointer; }
div { width:50px; height:30px; margin:5px; float:left;
background:green; }
span { color:red; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<span></span>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
7. get( ) Returns: Array<Element>
get( ), 실행후 원소 배열 반환
Access all matched DOM elements.
매치되는 모든 문서 원소들을 배열로 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
function disp(divs) {
var a = [];
for (var i = 0; i < divs.length; i++) {
a.push(divs[i].innerHTML);
}
$("span").text(a.join(" "));
}
disp( $("div").get().reverse() );
});
</script>
<style>
span { color:red; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
Reversed - <span></span>
<div>One</div>
<div>Two</div>
<div>Three</div>
</body>
</html>
8. get( index ) Returns: Element
get( 인덱스 ), 실행후 매치 되는 원소를 반환
Access a single matched DOM element at a specified index in the matched set.
매치되는 원소들 중 주어진 인덱스에 해당하는 하나의 원소만 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("*", document.body).click(function (e) {
e.stopPropagation();
var domEl = $(this).get(0);
$("span:first").text("Clicked on - " + domEl.tagName);
});
});
</script>
<style>
span { color:red; }
div { background:yellow; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<span> </span>
<p>In this paragraph is an <span>important</span> section</p>
<div><input type="text" /></div>
</body>
</html>
9. index( subject ) Returns: Number
index( 객체 ), 실행후 숫자를 반환
Searches every matched element for the object and returns the index of the element, if found, starting with zero.
매치되어진 원소들에 대해 주어진 객체와 동일한것을 검색하여,
존재하면 그 원소들중에 몇번째에 해당하는가 하는 인덱스 번호를 반환한다.
인덱스는 0부터 시작한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("div").click(function () {
// this is the dom element clicked
var index = $("div").index(this);
$("span").text("That was div index #" + index);
});
});
</script>
<style>
div { background:yellow; margin:5px; }
span { color:red; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<span>Click a div!</span>
<div>First div</div>
<div>Second div</div>
<div>Third div</div>
</body>
</html>
10. jQuery.fn.extend( object ) Returns: jQuery
jQuery.fn.extend( 객체), 실행후 jQuery객체를 반환
Extends the jQuery element set to provide new methods (used to make a typical jQuery plugin).
제이쿼리에 새로운 함수를 확장한다.(플러그인으로 만들어 사용한다.)
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
jQuery.fn.extend({
check: function() {
return this.each(function() { this.checked = true; });
},
uncheck: function() {
return this.each(function() { this.checked = false; });
}
});
$(function(){
$("#button1").click(function(){
$('input').check();
});
$("#button2").click(function(){
$('input').uncheck();
});
});
</script>
<style>
div { background:yellow; margin:5px; }
span { color:red; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form>
<input type="checkbox" name="">
<input type="checkbox" name="">
<input type="checkbox" name="">
<input type="checkbox" name="">
<input type="checkbox" name="">
<input type="checkbox" name="">
</form>
<input type='button' id='button1' value='전체선택'>
<input type='button' id='button2' value='전체해제'>
</body>
</html>
11. jQuery.extend( object ) Returns: jQuery
jQuery.fn.extend( 객체), 실행후 jQuery객체를 반환
Extends the jQuery object itself.
제이쿼리 자체를 확장
아직은 잘 모르겟음
14. jQuery.noConflict( ) Returns: jQuery
jQuery.noConflict( ), 실행후 jQuery객체를 반환
Run this function to give control of the $ variable back to whichever library first implemented it.
아직은 잘 모르겠음
15. jQuery.noConflict( extreme ) Returns: jQuery
jQuery.noConflict( extreme ), 실행후 jQuery객체를 반환
Revert control of both the $ and jQuery variables to their original owners. Use with discretion.
아직은 잘 모르겠음
<Selectors>=>객체 선책
1. #id Returns: Element
#아이디, 실행후 원소 반환
Matches a single element with the given id attribute.
주어진 아이디에 매치되는 원소하나를 찾아 반환
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("#myDiv").css("border","3px solid red");
});
</script>
<style>
div {
width: 90px;
height: 90px;
float:left;
padding: 5px;
margin: 5px;
background-color: #EEEEEE;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="notMe"><p>id="notMe"</p></div>
<div id="myDiv">id="myDiv"</div>
</body>
</html>
2. element Returns: Array<Element>
원소명, 실행후 원소 배열 반환
Matches all elements with the given name.
주어진 원소명에 매치되는 모든 원소를 배열로 반환
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("div").css("border","3px solid red");
});
</script>
<style>
div,span {
width: 60px;
height: 60px;
float:left;
padding: 10px;
margin: 10px;
background-color: #EEEEEE;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>DIV1</div>
<div>DIV2</div>
<span>SPAN</span>
</body>
</html>
3. .class Returns: Array<Element>
클래스명, 실행후 원소배열로 반환
Matches all elements with the given class.
주어진 클래스명에 매치되는 모든 원소를 배열로 반환
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$(".myClass").css("border","3px solid red");
});
</script>
<style>
div,span {
width: 150px;
height: 60px;
float:left;
padding: 10px;
margin: 10px;
background-color: #EEEEEE;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="notMe">div class="notMe"</div>
<div class="myClass">div class="myClass"</div>
<span class="myClass">span class="myClass"</span>
</body>
</html>
4. * Returns: Array<Element>
모든것, 실행후 원소 배열로 반환
Matches all elements.
매치되는 모든 원소를 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("*").css("border","3px solid red");
});
</script>
<style>
div,span,p {
width: 150px;
height: 60px;
float:left;
padding: 10px;
margin: 10px;
background-color: #EEEEEE;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>DIV</div>
<span>SPAN</span>
<p>P <button>Button</button></p>
</body>
</html>
5. selector1, selector2, selectorN Returns: Array<Element>
selector1, selector2, selectorN, 실행후 원소배열로 반환
Matches the combined results of all the specified selectors.
주어진 것들에 대해 매치되는 모든 원소를 배열로 반환
구분자는 ,
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("div,span,p.myClass").css("border","3px solid red");
});
</script>
<style>
div,span,p {
width: 130px;
height: 60px;
float:left;
padding: 3px;
margin: 2px;
background-color: #EEEEEE;
font-size:14px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>div</div>
<p class="myClass">p class="myClass"</p>
<p class="notMyClass">p class="notMyClass"</p>
<span>span</span>
</body>
</html>
6. ancestor descendant Returns: Array<Element>
조상 자손, 실행후 원소 배열로 반환
Matches all descendant elements specified by "descendant" of elements specified by "ancestor".
주어진 조상에 주어진 자손을 가진 모든 자손을 배열로 반환
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("form input").css("border", "2px dotted blue");
});
</script>
<style>
body { font-size:14px; }
form { border:2px green solid; padding:2px; margin:0;
background:#efe; }
div { color:red; }
fieldset { margin:1px; padding:3px; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form>
<div>Form is surrounded by the green outline</div>
<label>Child:</label>
<input name="name" />
<fieldset>
<label>Grandchild:</label>
<input name="newsletter" />
</fieldset>
</form>
Sibling to form: <input name="none" />
</body>
</html>
7. parent > child Returns: Array<Element>
조상 > 자손, 실행후 원소 배열 반환
Matches all child elements specified by "child" of elements specified by "parent".
주어진 조상에 포함된 주어진 자손에 매치되는 일단계 자손들만 모두 배열로 반환
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("#main > *").css("border", "3px double red");
});
</script>
<style>
body { font-size:14px; }
span#main { display:block; background:yellow; height:110px; }
button { display:block; float:left; margin:2px;
font-size:14px; }
div { width:90px; height:90px; margin:5px; float:left;
background:#bbf; font-weight:bold; }
div.mini { width:30px; height:30px; background:green; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<span id="main">
<div></div>
<button>Child</button>
<div class="mini"></div>
<div>
<div class="mini"></div>
<div class="mini"></div>
</div>
<div><button>Grand</button></div>
<div><span>A Span <em>in</em> child</span></div>
<span>A Span in main</span>
</span>
</body>
</html>
8. prev + next Returns: Array<Element>
앞 뒤, 실행후 원소배열 반환
Matches all next elements specified by "next" that are next to elements specified by "prev".
주어진 앞원소와 뒤원소에 순차적으로 매치 되는 뒤원소들을 모두 배열로 반환
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("label + input").css("color", "blue").val("Labeled!")
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<form>
<label>Name:</label>
<input name="name" />
<fieldset>
<label>Newsletter:</label>
<input name="newsletter" />
</fieldset>
</form>
<input name="none" />
</body>
</html>
9. prev ~ siblings Returns: Array<Element>
앞원소~형제 원소, 실행후 원소배열 반환
Matches all sibling elements after the "prev" element that match the filtering "siblings" selector.
주어진 앞원소와 형제인 뒤원소를 찾아 모두 배열로 반환
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("#prev ~ div").css("border", "3px groove blue");
});
</script>
<style>
div,span {
display:block;
width:80px;
height:80px;
margin:5px;
background:#bbffaa;
float:left;
font-size:14px;
}
div#small {
width:60px;
height:25px;
font-size:12px;
background:#fab;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>div (doesn't match since before #prev)</div>
<div id="prev">div#prev</div>
<div>div sibling</div>
<div>div sibling <div id="small">div neice</div></div>
<span>span sibling (not div)</span>
<div>div sibling</div>
</body>
</html>
10. :first Returns: Element
첫번째, 실행후 원소 반환
Matches the first selected element.
매치되는 원소들중 첫번째 것만 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("tr:first").css("font-style", "italic");
});
</script>
<style>
td { color:blue; font-weight:bold; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<table>
<tr><td>Row 1</td></tr>
<tr><td>Row 2</td></tr>
<tr><td>Row 3</td></tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
11. :last Returns: Element
마지막, 실행후 원소 반환
Matches the last selected element.
매치되는 원소들중 마지막 것만 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("tr:last").css({backgroundColor: 'yellow', fontWeight: 'bolder'});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<table>
<tr><td>First Row</td></tr>
<tr><td>Middle Row</td></tr>
<tr><td>Last Row</td></tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
12. :not(selector) Returns: Array<Element>
아니다, 실행후 원소 배열 반환
Filters out all elements matching the given selector.
주어진 것에 해당하지 않는 모든 것을 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("input:not(:checked) + span").css("background-color", "yellow");
$("input").attr("disabled", "disabled");
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<input type="checkbox" name="a" />
<span>Mary</span>
</div>
<div>
<input type="checkbox" name="b" />
<span>Paul</span>
</div>
<div>
<input type="checkbox" name="c" checked="checked" />
<span>Peter</span>
</div>
</body>
</html>
13. :even Returns: Array<Element>
짝수, 실행후 원소 배열 반환
Matches even elements, zero-indexed.
매치된 원소들 중에서 인덱스가 짝수인것 모두 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("tr:even").css("background-color", "#bbbbff");
});
</script>
<style>
table {
background:#eeeeee;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<table border="1">
<tr><td>Row with Index #0</td></tr>
<tr><td>Row with Index #1</td></tr>
<tr><td>Row with Index #2</td></tr>
<tr><td>Row with Index #3</td></tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
14. :odd Returns: Array<Element>
홀수, 실행후 원소 배열 반환
Matches odd elements, zero-indexed.
매치된 원소들 중에서 인덱스가 홀수인것 모두 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("tr:odd").css("background-color", "#bbbbff");
});
</script>
<style>
table {
background:#f3f7f5;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<table border="1">
<tr><td>Row with Index #0</td></tr>
<tr><td>Row with Index #1</td></tr>
<tr><td>Row with Index #2</td></tr>
<tr><td>Row with Index #3</td></tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
15. :eq(index) Returns: Element
eq(인덱스), 실행후 원소 반환
Matches a single element by its index.
매치된 원소들 중에서 주어진 인덱스에 매치되는 원소 한개를 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("td:eq(2)").css("text-decoration", "blink");
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<table border="1">
<tr><td>TD #0</td><td>TD #1</td><td>TD #2</td></tr>
<tr><td>TD #3</td><td>TD #4</td><td>TD #5</td></tr>
<tr><td>TD #6</td><td>TD #7</td><td>TD #8</td></tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
16. :gt(index) Returns: Array<Element>
초과, 실행후 원소 배열 반환
Matches all elements with an index above the given one.
매치된 원소들 중에서 인덱스로 주어진 것보다 큰 인덱스 들을 모두 배열로 반환
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("td:gt(4)").css("text-decoration", "line-through");
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<table border="1">
<tr><td>TD #0</td><td>TD #1</td><td>TD #2</td></tr>
<tr><td>TD #3</td><td>TD #4</td><td>TD #5</td></tr>
<tr><td>TD #6</td><td>TD #7</td><td>TD #8</td></tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
17. :lt(index) Returns: Array<Element>
미만, 실행후 원소 배열 반환
Matches all elements with an index below the given one.
매치된 원소들 중에서 인덱스로 주어진 것보다 작은 인덱스 들을 모두 배열로 반환
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("td:lt(4)").css("color", "red");
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<table border="1">
<tr><td>TD #0</td><td>TD #1</td><td>TD #2</td></tr>
<tr><td>TD #3</td><td>TD #4</td><td>TD #5</td></tr>
<tr><td>TD #6</td><td>TD #7</td><td>TD #8</td></tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
18. :header Returns: Array<Element>
헤더, 실행후 원소 배열 반환
Matches all elements that are headers, like h1, h2, h3 and so on.
매치되는 원소들 중에서 h1, h2 ... 와 같은 헤더 태그들을 모두 배열로 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$(":header").css({ background:'#CCC', color:'blue' });
});
</script>
<style>
body { font-size: 10px; font-family: Arial; }
h1, h2 { margin: 3px 0; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Header 1</h1>
<p>Contents 1</p>
<h2>Header 2</h2>
<p>Contents 2</p>
</body>
</html>
19. :animated Returns: Array<Element>
움직인다, 실행후 원소 배열 반환
Matches all elements that are currently being animated.
매치된 원소들 중에서 애니메이션이 동작하고 있는 것들을 모두 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("#run").click(function(){
$("div:animated").toggleClass("colored");
});
function animateIt() {
$("#mover").slideToggle("slow", animateIt);
}
animateIt();
});
</script>
<style>
div { background:yellow; border:1px solid #AAA; width:80px; height:80px; margin:5px; float:left; }
div.colored { background:green; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<button id="run">Run</button>
<div></div>
<div id="mover"></div>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
20. :contains(text) Returns: Array<Element>
포함, 실행후 원소 배열 반환
Matches elements which contain the given text.
매치된 원소들 중에서 주어진 텍스트를 포함하는 것들을 모두 배열로 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("div:contains('John')").css("text-decoration", "underline");
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div>John Resig</div>
<div>George Martin</div>
<div>Malcom John Sinclair</div>
<div>J. Ohn
</body>
</html>
21. :empty Returns: Array<Element>
비엇다. 실행후 원소 배열 반환
Matches all elements that are empty, be it elements or text.
매치된 원소들 중에서 텍스트가 비어있는 것들을 모두 배열로 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("td:empty").text("Was empty!").css('background', 'rgb(255,220,200)');
});
</script>
<style>
td { text-align:center; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<table border="1">
<tr><td>TD #0</td><td></td></tr>
<tr><td>TD #2</td><td></td></tr>
<tr><td></td><td>TD#5</td></tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
22. :has(selector) Returns: Array<Element>
has(selector), 실행후 원소 배열 반환
Matches elements which contain at least one element that matches the specified selector.
매치된 원소들 중에서 주어진 것을 포함하는 것을 모두 배열로 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("div:has(p)").addClass("test");
});
</script>
<style>
.test{ border: 3px inset red; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div><p>Hello in a paragraph</p></div>
<div>Hello again! (with no paragraph)</div>
</body>
</html>
23. :parent Returns: Array<Element>
부모, 실행후 원소 배열 반환
Matches all elements that are parents - they have child elements, including text.
주어진 것이 부모인 것을 모두 받아온다, 비어있는 것은 포함 안함
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("td:parent").fadeTo(1500, 0.3);
});
</script>
<style>
td { width:40px; background:green; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<table border="1">
<tr><td>Value 1</td><td></td></tr>
<tr><td>Value 2</td><td></td></tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
24. :hidden Returns: Array<Element>
안보임, 실행후 원소 배열 반환
Matches all elements that are hidden, or input elements of type "hidden".
보이지 않는 모든 것들을 반환한다. none hidden 등, 추가로 input을 지정하면 인풋타입이 히든인것만 받아온다
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
// in some browsers :hidden includes head, title, script, etc... so limit to body
$("span:first").text("Found " + $(":hidden", document.body).length +
" hidden elements total.");
$("div:hidden").show(3000);
$("span:last").text("Found " + $("input:hidden").length + " hidden inputs.");
});
</script>
<style>
div { width:70px; height:40px; background:#ee77ff; margin:5px; float:left; }
span { display:block; clear:left; color:red; }
.starthidden { display:none; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<span></span>
<div></div>
<div style="display:none;">Hider!</div>
<div></div>
<div class="starthidden">Hider!</div>
<div></div>
<form>
<input type="hidden" />
<input type="hidden" />
<input type="hidden" />
</form>
<span>
</span>
</body>
</html>
25. :visible Returns: Array<Element>
보임, 실행후 원소 배열 반환
Matches all elements that are visible.
보이는 것들을 모두 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("div:visible").click(function () {
$(this).css("background", "yellow");
});
$("button").click(function () {
$("div:hidden").show("fast");
});
});
</script>
<style>
div { width:50px; height:40px; margin:5px; border:3px outset green; float:left; }
.starthidden { display:none; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<button>Show hidden to see they don't change</button>
<div></div>
<div class="starthidden"></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div style="display:none;"></div>
</body>
</html>
26. [attribute] Returns: Array<Element>
속성, 실행후 원소 배열 반환
Matches elements that have the specified attribute.
주어진 속성을 가진 것들을 모두 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("div[id]").one("click", function(){
var idString = $(this).text() + " = " + $(this).attr("id");
$(this).text(idString);
});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div>no id</div>
<div id="hey">with id</div>
<div id="there">has an id</div>
<div>nope</div>
</body>
</html>
27. [attribute=value] Returns: Array<Element>
속성=값, 실행후 원소 배열 반환
Matches elements that have the specified attribute with a certain value.
주어진 속성과 주어진 값이 일치 하는 모든것들을 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("input[name='newsletter']").next().text(" is newsletter");
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<input type="radio" name="newsletter" value="Hot Fuzz" />
<span>name?</span>
</div>
<div>
<input type="radio" name="newsletter" value="Cold Fusion" />
<span>name?</span>
</div>
<div>
<input type="radio" name="accept" value="Evil Plans" />
<span>name?</span>
</div>
</body>
</html>
28. [attribute!=value] Returns: Array<Element>
속성!=값, 실행후 원소 배열 반환
Matches elements that don't have the specified attribute with a certain value.
주어진 속성과 주어진 값이 일치 하지 않는 모든것들을 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("input[name!='newsletter']").next().text(" is not newsletter");
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<input type="radio" name="newsletter" value="Hot Fuzz" />
<span>name?</span>
</div>
<div>
<input type="radio" name="newsletter" value="Cold Fusion" />
<span>name?</span>
</div>
<div>
<input type="radio" name="accept" value="Evil Plans" />
<span>name?</span>
</div>
</body>
</html>
29. [attribute^=value] Returns: Array<Element>
속성^=값, 실행후 원소 배열 반환
Matches elements that have the specified attribute and it starts with a certain value.
주어진 속성을 가지며 값이 주어진 값으로 시작되는 모든 것을 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("input[name^='news']").val("news here!");
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<input name="newsletter" />
<input name="milkman" />
<input name="newsboy" />
</body>
</html>
30. [attribute$=value] Returns: Array<Element>
속성$=값, 실행후 원소 배열 반환
Matches elements that have the specified attribute and it ends with a certain value.
주어진 속성을 가지며 값이 주어진 값으로 끝나는 모든 것을 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("input[name$='letter']").val("a letter");
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<input name="newsletter" />
<input name="milkman" />
<input name="jobletter" />
</body>
</html>
31. [attribute*=value] Returns: Array<Element>
속성*=값, 실행후 원소 배열 반환
Matches elements that have the specified attribute and it contains a certain value.
주어진 속성을 가지며 값이 주어진 값을 포함하는 모든 것을 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("input[name*='man']").val("has man in it!");
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<input name="man-news" />
<input name="milkman" />
<input name="letterman2" />
<input name="newmilk" />
</body>
</html>
32. [selector1][selector2][selectorN] Returns: Array<Element>
속성들, 실행후 원소 배열 반환
Matches elements that have the specified attribute and it contains a certain value.
속성을 여러개 지정할수도 있다. 매치되는 모든 것을 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("input[id][name$='man']").val("only this one");
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<input id="man-news" name="man-news" />
<input name="milkman" />
<input id="letterman" name="new-letterman" />
<input name="newmilk" />
</body>
</html>
33. :nth-child(index/even/odd/equation) Returns: Array<Element>
몇번째 자식, 실행후 원소 배열 반환
Matches the nth-child of its parent or all its even or odd children.
인덱스나 키워드로 자식을 지정하여 매치되는 것은 모두 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("ul li:nth-child(2)").append("<span> - 2nd!</span>");
});
</script>
<style>
div { float:left; }
span { color:blue; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div><ul>
<li>John</li>
<li>Karl</li>
<li>Brandon</li>
</ul></div>
<div><ul>
<li>Sam</li>
</ul></div>
<div><ul>
<li>Glen</li>
<li>Tane</li>
<li>Ralph</li>
<li>David</li>
</ul></div>
</body>
</html>
34. :first-child Returns: Array<Element>
첫번째 자식, 실행후 원소 배열 반환
Matches the first child of its parent.
첫번째 자식에 매치되는 모든 것을 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("div span:first-child")
.css("text-decoration", "underline")
.hover(function () {
$(this).addClass("sogreen");
}, function () {
$(this).removeClass("sogreen");
});
});
</script>
<style>
span { color:#008; }
span.sogreen { color:green; font-weight: bolder; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<span>John,</span>
<span>Karl,</span>
<span>Brandon</span>
</div>
<div>
<span>Glen,</span>
<span>Tane,</span>
<span>Ralph</span>
</div>
</body>
</html>
35. :last-child Returns: Array<Element>
마지막 자식, 실행후 원소 배열 반환
Matches the last child of its parent.
마지막 자식에 매치되는 모든 것을 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("div span:last-child")
.css({color:"red", fontSize:"80%"})
.hover(function () {
$(this).addClass("solast");
}, function () {
$(this).removeClass("solast");
});
});
</script>
<style>
span.solast { text-decoration:line-through; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<span>John,</span>
<span>Karl,</span>
<span>Brandon,</span>
<span>Sam</span>
</div>
<div>
<span>Glen,</span>
<span>Tane,</span>
<span>Ralph,</span>
<span>David</span>
</div>
</body>
</html>
36. :only-child Returns: Array<Element>
하나의 자식, 실행후 원소 배열 반환
Matches the only child of its parent.
하나의 자식으로만 이루어진 모든 것을 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("div button:only-child").text("Alone").css("border", "2px blue solid");
});
</script>
<style>
div { width:100px; height:80px; margin:5px; float:left; background:#b9e }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<button>Sibling!</button>
<button>Sibling!</button>
</div>
<div>
<button>Sibling!</button>
</div>
<div>
None
</div>
<div>
<button>Sibling!</button>
<button>Sibling!</button>
<button>Sibling!</button>
</div>
<div>
<button>Sibling!</button>
</div>
</body>
</html>
37. :input Returns: Array<Element>
인풋, 실행후 원소 배열 반환
Matches all input, textarea, select and button elements.
인풋, 텍스트에리어, 셀렉트박스, 버튼들을 모두 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
var allInputs = $(":input");
var formChildren = $("form > *");
$("div").text("Found " + allInputs.length + " inputs and the form has " +
formChildren.length + " children.")
.css("color", "red");
$("form").submit(function () { return false; }); // so it won't submit
});
</script>
<style>
textarea { height:45px; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form>
<input type="button" value="Input Button"/>
<input type="checkbox" />
<input type="file" />
<input type="hidden" />
<input type="image" />
<input type="password" />
<input type="radio" />
<input type="reset" />
<input type="submit" />
<input type="text" />
<select><option>Option<option/></select>
<textarea></textarea>
<button>Button</button>
</form>
<div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
38. :text Returns: Array<Element>
텍스트, 실행후 원소 배열 반환
Matches all input elements of type text.
인풋타입이 텍스트인 것을 모두 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
var input = $(":text").css({background:"yellow", border:"3px red solid"});
$("div").text("For this type jQuery found " + input.length + ".")
.css("color", "red");
$("form").submit(function () { return false; }); // so it won't submit
});
</script>
<style>
textarea { height:45px; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form>
<input type="button" value="Input Button"/>
<input type="checkbox" />
<input type="file" />
<input type="hidden" />
<input type="image" />
<input type="password" />
<input type="radio" />
<input type="reset" />
<input type="submit" />
<input type="text" />
<select><option>Option<option/></select>
<textarea></textarea>
<button>Button</button>
</form>
<div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
39. :password Returns: Array<Element>
패스워드, 실행후 원소 배열 반환
Matches all input elements of type password.
인풋타입이 패스워드인 것을 모두 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
var input = $(":password").css({background:"yellow", border:"3px red solid"});
$("div").text("For this type jQuery found " + input.length + ".")
.css("color", "red");
$("form").submit(function () { return false; }); // so it won't submit
});
</script>
<style>
textarea { height:45px; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form>
<input type="button" value="Input Button"/>
<input type="checkbox" />
<input type="file" />
<input type="hidden" />
<input type="image" />
<input type="password" />
<input type="radio" />
<input type="reset" />
<input type="submit" />
<input type="text" />
<select><option>Option<option/></select>
<textarea></textarea>
<button>Button</button>
</form>
<div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
40. :radio Returns: Array<Element>
레디오, 실행후 원소 배열 반환
Matches all input elements of type radio.
인풋타입이 레디오인 것을 모두 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
var input = $(":radio").css({background:"yellow", border:"3px red solid"});
$("div").text("For this type jQuery found " + input.length + ".")
.css("color", "red");
$("form").submit(function () { return false; }); // so it won't submit
});
</script>
<style>
textarea { height:45px; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form>
<input type="button" value="Input Button"/>
<input type="checkbox" />
<input type="file" />
<input type="hidden" />
<input type="image" />
<input type="password" />
<input type="radio" name="asdf" />
<input type="radio" name="asdf" />
<input type="reset" />
<input type="submit" />
<input type="text" />
<select><option>Option<option/></select>
<textarea></textarea>
<button>Button</button>
</form>
<div>
</div>
</body>
41. :checkbox Returns: Array<Element>
체크박스, 실행후 원소 배열 반환
Matches all input elements of type checkbox.
인풋타입이 체크박스인 것을 모두 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
var input = $(":checkbox").css({background:"yellow", border:"3px red solid"});
$("div").text("For this type jQuery found " + input.length + ".")
.css("color", "red");
$("form").submit(function () { return false; }); // so it won't submit
});
</script>
<style>
textarea { height:45px; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form>
<input type="button" value="Input Button"/>
<input type="checkbox" />
<input type="checkbox" />
<input type="file" />
<input type="hidden" />
<input type="image" />
<input type="password" />
<input type="radio" />
<input type="reset" />
<input type="submit" />
<input type="text" />
<select><option>Option<option/></select>
<textarea></textarea>
<button>Button</button>
</form>
<div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
42. :submit Returns: Array<Element>
서브밋, 실행후 원소 배열 반환
Matches all input elements of type submit.
인풋타입이 서브밋인 것을 모두 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
var input = $(":submit").css({background:"yellow", border:"3px red solid"});
$("div").text("For this type jQuery found " + input.length + ".")
.css("color", "red");
$("form").submit(function () { return false; }); // so it won't submit
});
</script>
<style>
textarea { height:45px; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form>
<input type="button" value="Input Button"/>
<input type="checkbox" />
<input type="file" />
<input type="hidden" />
<input type="image" />
<input type="password" />
<input type="radio" />
<input type="reset" />
<input type="submit" />
<input type="text" />
<select><option>Option<option/></select>
<textarea></textarea>
<button>Button</button>
</form>
<div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
43. :image Returns: Array<Element>
이미지, 실행후 원소 배열 반환
Matches all input elements of type image.
인풋타입이 이미지인 것을 모두 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
var input = $(":image").css({background:"yellow", border:"3px red solid"});
$("div").text("For this type jQuery found " + input.length + ".")
.css("color", "red");
$("form").submit(function () { return false; }); // so it won't submit
});
</script>
<style>
textarea { height:45px; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form>
<input type="button" value="Input Button"/>
<input type="checkbox" />
<input type="file" />
<input type="hidden" />
<input type="image" />
<input type="password" />
<input type="radio" />
<input type="reset" />
<input type="submit" />
<input type="text" />
<select><option>Option<option/></select>
<textarea></textarea>
<button>Button</button>
</form>
<div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
44. :reset Returns: Array<Element>
리셋, 실행후 원소 배열 반환
Matches all input elements of type reset.
인풋타입이 리셋인 것을 모두 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
var input = $(":reset").css({background:"yellow", border:"3px red solid"});
$("div").text("For this type jQuery found " + input.length + ".")
.css("color", "red");
$("form").submit(function () { return false; }); // so it won't submit
});
</script>
<style>
textarea { height:45px; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form>
<input type="button" value="Input Button"/>
<input type="checkbox" />
<input type="file" />
<input type="hidden" />
<input type="image" />
<input type="password" />
<input type="radio" />
<input type="reset" />
<input type="submit" />
<input type="text" />
<select><option>Option<option/></select>
<textarea></textarea>
<button>Button</button>
</form>
<div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
45. :button Returns: Array<Element>
버튼, 실행후 원소 배열 반환
Matches all input elements of type button.
인풋타입이 버튼인 것을 모두 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
var input = $(":button").css({background:"yellow", border:"3px red solid"});
$("div").text("For this type jQuery found " + input.length + ".")
.css("color", "red");
$("form").submit(function () { return false; }); // so it won't submit
});
</script>
<style>
textarea { height:45px; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form>
<input type="button" value="Input Button"/>
<input type="checkbox" />
<input type="file" />
<input type="hidden" />
<input type="image" />
<input type="password" />
<input type="radio" />
<input type="reset" />
<input type="submit" />
<input type="text" />
<select><option>Option<option/></select>
<textarea></textarea>
<button>Button</button>
</form>
<div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
46. :file Returns: Array<Element>
파일, 실행후 원소 배열 반환
Matches all input elements of type file.
인풋타입이 파일인 것을 모두 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
var input = $(":file").css({background:"yellow", border:"3px red solid"});
$("div").text("For this type jQuery found " + input.length + ".")
.css("color", "red");
$("form").submit(function () { return false; }); // so it won't submit
});
</script>
<style>
textarea { height:45px; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form>
<input type="button" value="Input Button"/>
<input type="checkbox" />
<input type="file" />
<input type="hidden" />
<input type="image" />
<input type="password" />
<input type="radio" />
<input type="reset" />
<input type="submit" />
<input type="text" />
<select><option>Option<option/></select>
<textarea></textarea>
<button>Button</button>
</form>
<div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
47. :hidden Returns: Array<Element>
히든, 실행후 원소 배열 반환
Matches all elements that are hidden, or input elements of type "hidden".
인풋타입이 히든인 것을 모두 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
// in some browsers :hidden includes head, title, script, etc... so limit to body
$("span:first").text("Found " + $(":hidden", document.body).length +
" hidden elements total.");
$("div:hidden").show(3000);
$("span:last").text("Found " + $("input:hidden").length + " hidden inputs.");
});
</script>
<style>
div { width:70px; height:40px; background:#ee77ff; margin:5px; float:left; }
span { display:block; clear:left; color:red; }
.starthidden { display:none; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<span></span>
<div></div>
<div style="display:none;">Hider!</div>
<div></div>
<div class="starthidden">Hider!</div>
<div></div>
<form>
<input type="hidden" />
<input type="hidden" />
<input type="hidden" />
</form>
<span>
</span>
</body>
</html>
48. :enabled Returns: Array<Element>
활성화? 사용가능?, 실행후 원소 배열 반환
Matches all elements that are enabled.
활성화된 모든 것들을 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("input:enabled").val("this is it");
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<form>
<input name="email" disabled="disabled" />
<input name="id" />
</form>
</body>
</html>
49. :disabled Returns: Array<Element>
비활성화? 사용불가능?, 실행후 원소 배열 반환
Matches all elements that are disabled.
비활성화된 모든 것들을 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("input:disabled").val("this is it");
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<form>
<input name="email" disabled="disabled" />
<input name="id" />
</form>
</body>
</html>
50. :checked Returns: Array<Element>
체크됏음, 실행후 원소 배열 반환
Matches all elements that are checked.
인풋이 체크된 모든 것들을 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
function countChecked() {
var n = $("input:checked").length;
$("div").text(n + (n == 1 ? " is" : " are") + " checked!");
}
countChecked();
$(":checkbox").click(countChecked);
});
</script>
<style>
div { color:red; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form>
<input type="checkbox" name="newsletter" checked="checked" value="Hourly" />
<input type="checkbox" name="newsletter" value="Daily" />
<input type="checkbox" name="newsletter" value="Weekly" />
<input type="checkbox" name="newsletter" checked="checked" value="Monthly" />
<input type="checkbox" name="newsletter" value="Yearly" />
</form>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
51. :selected Returns: Array<Element>
선택되어짐, 실행후 원소 배열 반환
Matches all elements that are selected.
선택된 모든 것을 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("select").change(function () {
var str = "";
$("select option:selected").each(function () {
str += $(this).text() + " ";
});
$("div").text(str);
})
.trigger('change');
});
</script>
<style>
div { color:red; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<select name="garden" multiple="multiple">
<option>Flowers</option>
<option selected="selected">Shrubs</option>
<option>Trees</option>
<option selected="selected">Bushes</option>
<option>Grass</option>
<option>Dirt</option>
</select>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
<Attributes>
1. attr( name ) Returns: Object
속성 실행후 객체 반환
Access a property on the first matched element. This method makes it easy to retrieve a property value from the first matched element. If the element does not have an attribute with such a name, undefined is returned.
주어진 속성명의 값을 가져옴, 매치되는 첫번째 것만 가져옴
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
var title = $("em").attr("title");
$("div").text(title);
});
</script>
<style>
em { color:blue; font-weight;bold; }
div { color:red; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>
Once there was a <em title="huge, gigantic">large</em> dinosaur...
</p>
The title of the emphasis is:<div></div>
</body>
</html>
2. attr( properties ) Returns: jQuery
attr(속성배열) 실행후 jQuery객체를 반환
Set a key/value object as properties to all matched elements.
속성과 값들의 배열을 지정하여 적용
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("img").attr({
src: "/images/hat.gif",
title: "jQuery",
alt: "jQuery Logo"
});
$("div").text($("img").attr("alt"));
});
</script>
<style>
img { padding:10px; }
div { color:red; font-size:24px; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<img />
<img />
<img />
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
3. attr( key, value ) Returns: jQuery
attr( 속성, 값 ) 실행후 jQuery객체를 반환
Set a single property to a value, on all matched elements.
하나의 속성과 하나의 값만 지정하여 적용
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("button:gt(0)").attr("disabled","disabled");
});
</script>
<style>
button { margin:10px; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<button>0th Button</button>
<button>1st Button</button>
<button>2nd Button</button>
</body>
</html>
4. attr( key, fn ) Returns: jQuery
attr(속성, 콜백함수) 실행후 jQuery 객체를 반환
Set a single property to a computed value, on all matched elements.
하나의 속성과 콜백함수를 지정하여 적용
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("img").attr("src", function() {
return "/images/" + this.title;
});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<img title="hat.gif"/>
<img title="hat-old.gif"/>
<img title="hat2-old.gif"/>
</body>
</html>
5. removeAttr( name ) Returns: jQuery
속성 제거 실행후 jQuery 객체를 반환
Remove an attribute from each of the matched elements.
주어진 이름과 매치되는 속성을 제거
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("button").click(function () {
$(this).next().removeAttr("disabled")
.focus()
.val("editable now");
});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<button>Enable</button>
<input type="text" disabled="disabled" value="can't edit this" />
</body>
</html>
6. addClass( class ) Returns: jQuery
클래스 추가 실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Adds the specified class(es) to each of the set of matched elements.
주어진 클래스 적용
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("p:last").addClass("selected");
});
</script>
<style>
p { margin: 8px; font-size:16px; }
.selected { color:red; }
.highlight { background:yellow; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>Hello</p>
<p>and</p>
<p>Goodbye</p>
</body>
</html>
7. removeClass( class ) Returns: jQuery
클래스 제거 실행후 JQuery 객체를 리턴
Removes all or the specified class(es) from the set of matched elements.
주어진 클래스 제거
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("p:even").removeClass("blue");
});
</script>
<style>
p { margin: 4px; font-size:16px; font-weight:bolder; }
.blue { color:blue; }
.under { text-decoration:underline; }
.highlight { background:yellow; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p class="blue under">Hello</p>
<p class="blue under highlight">and</p>
<p class="blue under">then</p>
<p class="blue under">Goodbye</p>
</body>
</html>
8. toggleClass( class ) Returns: jQuery
클래스 추가 삭제 반복 실행후 jQuery 객체 리턴
Adds the specified class if it is not present, removes the specified class if it is present.
주어진 클래스를 추가 삭제를 반복한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("p").click(function () {
$(this).toggleClass("highlight");
});
});
</script>
<style>
p { margin: 4px; font-size:16px; font-weight:bolder;
cursor:pointer; }
.blue { color:blue; }
.highlight { background:yellow; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p class="blue">Click to toggle</p>
<p class="blue highlight">highlight</p>
<p class="blue">on these</p>
<p class="blue">paragraphs</p>
</body>
</html>
9. html( ) Returns: String
실행후 문자열을 반환
Get the html contents (innerHTML) of the first matched element. This property is not available on XML documents (although it will work for XHTML documents).
선택되어진 객체의 html을 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("p").click(function () {
var htmlStr = $(this).html();
$(this).text(htmlStr);
});
});
</script>
<style>
p { margin:8px; font-size:20px; color:blue;
cursor:pointer; }
b { text-decoration:underline; }
button { cursor:pointer; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>
<b>Click</b> to change the <span id="tag">html</span>
</p>
<p>
to a <span id="text">text</span> node.
</p>
<p>
This <button name="nada">button</button> does nothing.
</p>
</body>
</html>
10. html( val ) Returns: jQuery
실행후 jQuery 객체를 반환
Set the html contents of every matched element. This property is not available on XML documents (although it will work for XHTML documents).
매치되는 모든 원소에 주어진 html을 넣는다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("div").html("<span class='red'>Hello <b>Again</b></span>");
});
</script>
<style>
.red { color:red; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<span>Hello</span>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
11. text( ) Returns: String
실행후 문자열 반환
Get the text contents of all matched elements.
선택되어진 객체의 문자열을 반환한다. 태그는 제외된다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
var str = $("p:first").text();
$("p:last").html(str);
});
</script>
<style>
p { color:blue; margin:8px; }
b { color:red; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p><b>Test</b> Paragraph.</p>
<p></p>
</body>
</html>
12. text( val ) Returns: jQuery
실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Set the text contents of all matched elements.
매치되는 모든 원소에 주어진 텍스트를 집어넣는다. html을 넣는다 해도 텍스트화 된다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("p").text("<b>Some</b> new text.");
});
</script>
<style>
p { color:blue; margin:8px; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>Test Paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
13. val( ) Returns: String, Array
실행후 문자열이나 배열로 반환
Get the content of the value attribute of the first matched element.
첫번째 매치되는 원소의 값을 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
function displayVals() {
var singleValues = $("#single").val();
var multipleValues = $("#multiple").val() || [];
$("p").html("<b>Single:</b> " +
singleValues +
" <b>Multiple:</b> " +
multipleValues.join(", "));
}
$("select").change(displayVals);
displayVals();
});
</script>
<style>
p { color:red; margin:4px; }
b { color:blue; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p></p>
<select id="single">
<option>Single</option>
<option>Single2</option>
</select>
<select id="multiple" multiple="multiple">
<option selected="selected">Multiple</option>
<option>Multiple2</option>
<option selected="selected">Multiple3</option>
</select>
</body>
</html>
14. val( val ) Returns: jQuery
jQuery 객체를 반환
Set the value attribute of every matched element.
매치되는 모든 원소에 주어진 값을 적용한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("button").click(function () {
var text = $(this).text();
$("input").val(text);
});
});
</script>
<style>
button { margin:4px; cursor:pointer; }
input { margin:4px; color:blue; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<button>Feed</button>
<button>the</button>
<button>Input</button>
</div>
<input type="text" value="click a button" />
</body>
</html>
15. val( val )
반환 없음
Checks, or selects, all the radio buttons, checkboxes, and select options that match the set of values.
체크 박스, 셀렉트 박스 레디오 버튼 셀렉트 옵션 등에 값을 적용
레디오나 체크박스 같은 경우는 값을 여러개 지정하여 할수 있다.
멀티플 같은 경우 배열로서 값을 지정할수 있다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("#single").val("Single2");
$("#multiple").val(["Multiple2", "Multiple3"]);
$("input").val(["check2", "radio1"]);
});
</script>
<style>
body { color:blue; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<select id="single">
<option>Single</option>
<option>Single2</option>
</select>
<select id="multiple" multiple="multiple">
<option selected="selected">Multiple</option>
<option>Multiple2</option>
<option selected="selected">Multiple3</option>
</select><br/>
<input type="checkbox" value="check1"/> check1
<input type="checkbox" value="check2"/> check2
<input type="radio" name="r" value="radio1"/> radio1
<input type="radio" name="r" value="radio2"/> radio2
</body>
</html>
<Traversing>
1. eq( index ) Returns: jQuery
eq(인덱스) 실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Reduce the set of matched elements to a single element.
매치되는 원소중 인덱스와 일치하는 것 하나만 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("div").eq(2).addClass("red");
});
</script>
<style>
div { width:60px; height:60px; margin:10px; float:left;
border:2px solid blue; }
.red { background:red; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
2. hasClass( class ) Returns: Boolean
클래스가 있나 없나 실행후 참거짓 리턴
Checks the current selection against a class and returns true, if at least one element of the selection has the given class.
매치되는 원소에 주어진 클래스가 존재하면 참, 아니면 거짓을 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("div").click(function(){
if ( $(this).hasClass("protected") )
$(this).animate({ left: -10 }, 75)
.animate({ left: 10 }, 75)
.animate({ left: -10 }, 75)
.animate({ left: 10 }, 75)
.animate({ left: 0 }, 75);
});
});
</script>
<style>
div { width: 80px; height: 80px; background: #abc;
position: relative; border: 2px solid black;
margin: 20px 0px; float: left; left:0 }
div.protected { border-color: red; }
span { display:block; float:left; width:20px;
height:20px; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<span></span><div class="protected"></div>
<span></span><div></div>
<span></span><div></div>
<span></span><div class="protected"></div>
</body>
</html>
3. filter( expr ) Returns: jQuery
실행후 jQuery 객체를 반환
Removes all elements from the set of matched elements that do not match the specified expression(s).
매치되는 원소들중 해당 필터 표현에 맞지 않는 것들은 제거하고 반환
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("div").css("background", "#c8ebcc")
.filter(".middle")
.css("border-color", "red");
});
</script>
<style>
div { width:60px; height:60px; margin:5px; float:left;
border:2px white solid;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
<div class="middle"></div>
<div class="middle"></div>
<div class="middle"></div>
<div class="middle"></div>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
4. filter( fn ) Returns: jQuery
filter(함수) 실행후 jQuery 객체를 반환
Removes all elements from the set of matched elements that does not match the specified function.
매치되는 원소들중 해당 필터 함수에 맞지 않는 것들은 제거하고 반환
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("div").css("background", "#b4b0da")
.filter(function (index) {
return index == 1 || $(this).attr("id") == "fourth";
})
.css("border", "3px double red");
});
</script>
<style>
div { width:60px; height:60px; margin:5px; float:left;
border:3px white solid; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="first"></div>
<div id="second"></div>
<div id="third"></div>
<div id="fourth"></div>
<div id="fifth"></div>
<div id="sixth"></div>
</body>
</html>
5. is( expr ) Returns: Boolean
존재 여부 실행후 참거짓 반환
Checks the current selection against an expression and returns true, if at least one element of the selection fits the given expression.
매치되는 원소들중 주어진 표현식과 비교하여 일치 하면 참, 그렇지 않으면 거짓을 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("div").one('click', function () {
if ($(this).is(":first-child")) {
$("p").text("It's the first div.");
} else if ($(this).is(".blue,.red")) {
$("p").text("It's a blue or red div.");
} else if ($(this).is(":contains('Peter')")) {
$("p").text("It's Peter!");
} else {
$("p").html("It's nothing <em>special</em>.");
}
$("p").hide().slideDown("slow");
$(this).css({"border-style": "inset", cursor:"default"});
});
});
</script>
<style>
div { width:60px; height:60px; margin:5px; float:left;
border:4px outset; background:green; text-align:center;
font-weight:bolder; cursor:pointer; }
.blue { background:blue; }
.red { background:red; }
span { color:white; font-size:16px; }
p { color:red; font-weight:bolder; background:yellow;
margin:3px; clear:left; display:none; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
<div class="blue"></div>
<div></div>
<div class="red"></div>
<div><br/><span>Peter</span></div>
<div class="blue"></div>
<p> </p>
</body>
</html>
16. map( callback ) Returns: jQuery
map(콜백함수) 실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Translate a set of elements in the jQuery object into another set of values in an array (which may, or may not, be elements).
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("p").append( $("input").map(function(){
return $(this).val();
}).get().join(", ") );
});
</script>
<style>
p { color:red; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p><b>Values: </b></p>
<form>
<input type="text" name="name" value="John"/>
<input type="text" name="password" value="password"/>
<input type="text" name="url" value="http://ejohn.org/"/>
</form>
</body>
</html>
17. not( expr ) Returns: jQuery
실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Removes elements matching the specified expression from the set of matched elements.
매치되는 원소들중 표현식과 일치 하는 원소는 제거 하고 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("div").not(".green, #blueone")
.css("border-color", "red");
});
</script>
<style>
div { width:60px; height:60px; margin:10px; float:left;
background:yellow; border:2px solid white; }
.green { background:#8f8; }
.gray { background:#ccc; }
#blueone { background:#99f; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
<div id="blueone"></div>
<div></div>
<div class="green"></div>
<div class="green"></div>
<div class="gray"></div>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
18. slice( start, end ) Returns: jQuery
Selects a subset of the matched elements.
매치되어진 원소들 중에서 해당 시작인덱스와 끝 인덱스의 범위에 있는 인덱스의 원소들을 모두 배열로 반환한다.
끝 인덱스를 지정하지 않으면 시작인덱스 부터 끝까지 배열로 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
function colorEm() {
var $div = $("div");
var start = Math.floor(Math.random() *
$div.length);
var end = Math.floor(Math.random() *
($div.length - start)) +
start + 1;
if (end == $div.length) end = undefined;
$div.css("background", "");
if (end)
$div.slice(start, end).css("background", "yellow");
else
$div.slice(start).css("background", "yellow");
$("span").text('$("div").slice(' + start +
(end ? ', ' + end : '') +
').css("background", "yellow");');
}
$("button").click(colorEm);
});
</script>
<style>
div { width:40px; height:40px; margin:10px; float:left;
border:2px solid blue; }
span { color:red; font-weight:bold; }
button { margin:5px; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<button>Turn slice yellow</button>
<span>Click the button!</span>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
19. add( expr ) Returns: jQuery
add( expr ), 실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Adds more elements, matched by the given expression, to the set of matched elements.
매치된 원소에 새로운 원소나 원소들을 추가한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("div").css("border", "2px solid red")
.add("p")
.css("background", "yellow");
});
</script>
<style>
div { width:60px; height:60px; margin:10px; float:left; }
p { clear:left; font-weight:bold; font-size:16px;
color:blue; margin:0 10px; padding:2px; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<p>Added this... (notice no border)</p>
</body>
</html>
20. children( expr ) Returns: jQuery
children( expr ), 실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Get a set of elements containing all of the unique children of each of the matched set of elements.
선택되어진 원소의 자식들을 반환
이해가 잘 안됨
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("#container").click(function (e) {
$("*").removeClass("hilite");
var $kids = $(e.target).children();
var len = $kids.addClass("hilite").length;
$("#results span:first").text(len);
$("#results span:last").text(e.target.tagName);
e.preventDefault();
return false;
});
});
</script>
<style>
body { font-size:16px; font-weight:bolder; }
div { width:130px; height:82px; margin:10px; float:left;
border:1px solid blue; padding:4px; }
#container { width:auto; height:105px; margin:0; float:none;
border:none; }
.hilite { border-color:red; }
#results { display:block; color:red; }
p { margin:10px; border:1px solid transparent; }
span { color:blue; border:1px solid transparent; }
input { width:100px; }
em { border:1px solid transparent; }
a { border:1px solid transparent; }
b { border:1px solid transparent; }
button { border:1px solid transparent; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="container">
<div>
<p>This <span>is the <em>way</em> we</span>
write <em>the</em> demo,</p>
</div>
<div>
<a href="#"><b>w</b>rit<b>e</b></a> the <span>demo,</span> <button>write
the</button> demo,
</div>
<div>
This <span>the way we <em>write</em> the <em>demo</em> so</span>
<input type="text" value="early" /> in
</div>
<p>
<span>t</span>he <span>m</span>orning.
<span id="results">Found <span>0</span> children in <span>TAG</span>.</span>
</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
21. contents( ) Returns: jQuery
contents( ), 실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Find all the child nodes inside the matched elements (including text nodes), or the content document, if the element is an iframe.
매치된 원소들중에서 비어있지 않는 자식들을 모두 가져옴
이해가 잘 안됨
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("p").contents().not("[@nodeType=1]").wrap("<b/>");
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<p>Hello <a href="Johnhttp://ejohn.org/">John</a>, how are you doing?</p>
</body>
</html>
22. find( expr ) Returns: jQuery
find( expr ), 실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Searches for all elements that match the specified expression. This method is a good way to find additional descendant elements with which to process.
매치되어진 원소들 중에서 주어진 것에 매치되는 것을 찾아 그것들을 모두 배열로 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("p").find("span").css('color','red');
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<p><span>Hello</span>, how are you?</p>
<p>Me? I'm <span>good</span>.</p>
</body>
</html>
23. next( expr ) Returns: jQuery
next( expr ), 실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Get a set of elements containing the unique next siblings of each of the matched set of elements.
매치되어진 원소와 형제 관계인 바로 다음 원소를 찾아 객체로 반환
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("button").click(function () {
var txt = $(this).text();
$(this).next().text(txt);
});
});
</script>
<style>
span { color:blue; font-weight:bold; }
button { width:100px; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div><button>First</button> - <span></span></div>
<div><button>Second</button> - <span></span></div>
<div><button>Third</button> - <span></span></div>
</body>
</html>
24. nextAll( expr ) Returns: jQuery
nextAll( expr ), 실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Find all sibling elements after the current element.
현재 매치되어진 원소와 형제 관계에 있는 모든 원소를 찾아 객체로 반환
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("div:first").nextAll().addClass("after");
});
</script>
<style>
div { width: 80px; height: 80px; background: #abc;
border: 2px solid black; margin: 10px; float: left; }
div.after { border-color: red; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
25. parent( expr ) Returns: jQuery
parent( expr ), 실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Get a set of elements containing the unique parents of the matched set of elements.
매치되어진 원소의 유일한 부모를 찾아 객체로 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("*", document.body).each(function () {
var parentTag = $(this).parent().get(0).tagName;
$(this).prepend(document.createTextNode(parentTag + " > "));
});
});
</script>
<style>
div,p { margin:10px; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>div,
<span>span, </span>
<b>b </b>
</div>
<p>p,
<span>span,
<em>em </em>
</span>
</p>
<div>div,
<strong>strong,
<span>span, </span>
<em>em,
<b>b, </b>
</em>
</strong>
<b>b </b>
</div>
</body>
</html>
26. parents( expr ) Returns: jQuery
parents( expr ), 실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Get a set of elements containing the unique ancestors of the matched set of elements (except for the root element).
매치되어진 원소의 유일한 조상들을 찾아 객체로 반환한다.
The matched elements can be filtered with an optional expression.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
var parentEls = $("b").parents()
.map(function () {
return this.tagName;
})
.get().join(", ");
$("b").append("<strong>" + parentEls + "</strong>");
});
</script>
<style>
b { color:blue; }
strong { color:red; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<p>
<span>
<b>My parents are: </b>
</span>
</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
27. prev( expr ) Returns: jQuery
prev( expr ), 실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Get a set of elements containing the unique previous siblings of each of the matched set of elements.
매치되어진 원소 보다 앞에 있는 유니크한 형제 원소를 찾아 객체로 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
var $curr = $("#start");
$curr.css("background", "#f99");
$("button").click(function () {
$curr = $curr.prev();
$("div").css("background", "");
$curr.css("background", "#f99");
});
});
</script>
<style>
div { width:40px; height:40px; margin:10px;
float:left; border:2px blue solid;
padding:2px; }
span { font-size:14px; }
p { clear:left; margin:10px; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div><span>has child</span></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div id="start"></div>
<div></div>
<p><button>Go to Prev</button></p>
</body>
</html>
28. prevAll( expr ) Returns: jQuery
prevAll( expr ), 실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Find all sibling elements before the current element.
매치되어진 원소보다 이전에 있는 모든 형제 원소를 찾아 객체로 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("div:last").prevAll().addClass("before");
});
</script>
<style>
div { width:70px; height:70px; background:#abc;
border:2px solid black; margin:10px; float:left; }
div.before { border-color: red; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
29. siblings( expr ) Returns: jQuery
siblings( expr ), 실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Get a set of elements containing all of the unique siblings of each of the matched set of elements.
매치되어진 원소들의 모든 형제 원소들을 찾아 반환한다.
Can be filtered with an optional expressions.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
var len = $(".hilite").siblings()
.css("color", "red")
.length;
$("b").text(len);
});
</script>
<style>
ul { float:left; margin:5px; font-size:16px; font-weight:bold; }
p { color:blue; margin:10px 20px; font-size:16px; padding:5px;
font-weight:bolder; }
.hilite { background:yellow; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li>One</li>
<li>Two</li>
<li class="hilite">Three</li>
<li>Four</li>
</ul>
<ul>
<li>Five</li>
<li>Six</li>
<li>Seven</li>
</ul>
<ul>
<li>Eight</li>
<li class="hilite">Nine</li>
<li>Ten</li>
<li class="hilite">Eleven</li>
</ul>
<p>Unique siblings: <b></b></p>
</body>
</html>
30. andSelf( ) Returns: jQuery
andSelf( ), 실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Add the previous selection to the current selection.
매치되어진 원소들의 상위의 형제 원소들과 조상 원소 모두를 찾아 추가하여 객체로 반환한다.
이해가 잘 안됨
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("div").find("p").andSelf().addClass("border");
$("div").find("p").addClass("background");
});
</script>
<style>
p, div { margin:5px; padding:5px; }
.border { border: 2px solid red; }
.background { background:yellow; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<p>First Paragraph</p>
<p>Second Paragraph</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
31. end( ) Returns: jQuery
end( ), 실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Revert the most recent 'destructive' operation, changing the set of matched elements to its previous state (right before the destructive operation).
현재 보다 이전의 매치상태로 돌아가서 객체를 반환
잘 이해가 안됨
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
jQuery.fn.showTags = function (n) {
var tags = this.map(function () {
return this.tagName;
})
.get().join(", ");
$("b:eq(" + n + ")").text(tags);
return this;
};
$("p").showTags(0)
.find("span")
.showTags(1)
.css("background", "yellow")
.end()
.showTags(2)
.css("font-style", "italic");
});
</script>
<style>
p, div { margin:1px; padding:1px; font-weight:bold;
font-size:16px; }
div { color:blue; }
b { color:red; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>
Hi there <span>how</span> are you <span>doing</span>?
</p>
<p>
This <span>span</span> is one of
several <span>spans</span> in this
<span>sentence</span>.
</p>
<div>
Tags in jQuery object initially: <b></b>
</div>
<div>
Tags in jQuery object after find: <b></b>
</div>
<div>
Tags in jQuery object after end: <b></b>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<Manipulation>
1. html( ) Returns: String
html( ), 실행후 문자열 반환
Get the html contents (innerHTML) of the first matched element. This property is not available on XML documents (although it will work for XHTML documents).
매치되어진 첫번째 원소의 html을 가져와서 반환
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("p").click(function () {
var htmlStr = $(this).html();
$(this).text(htmlStr);
});
});
</script>
<style>
p { margin:8px; font-size:20px; color:blue;
cursor:pointer; }
b { text-decoration:underline; }
button { cursor:pointer; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>
<b>Click</b> to change the <span id="tag">html</span>
</p>
<p>
to a <span id="text">text</span> node.
</p>
<p>
This <button name="nada">button</button> does nothing.
</p>
</body>
</html>
2. html( val ) Returns: jQuery
html( val ), 실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Set the html contents of every matched element. This property is not available on XML documents (although it will work for XHTML documents).
매치되는 모든 원소들에게 주어진 html을 삽입하고 객체를 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("div").html("<span class='red'>Hello <b>Again</b></span>");
});
</script>
<style>
.red { color:red; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<span>Hello</span>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
3. text( ) Returns: String
text( ), 실행후 문자열 반환
Get the text contents of all matched elements.
매치되어진 원소의 태그를 제외한 문자열만 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
var str = $("p:first").text();
$("p:last").html(str);
});
</script>
<style>
p { color:blue; margin:8px; }
b { color:red; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p><b>Test</b> Paragraph.</p>
<p></p>
</body>
</html>
4. text( val ) Returns: jQuery
text( val ), 실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Set the text contents of all matched elements.
매치된 원소들에 주어진 문자열을 삽입하고 객체를 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("p").text("<b>Some</b> new text.");
});
</script>
<style>
p { color:blue; margin:8px; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>Test Paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
5. append( content ) Returns: jQuery
append( content ) , 실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Append content to the inside of every matched element.
매치되어진 원소에 주어진 내용을 추가로 삽입한 후 객체 반환
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("p").append("<b>Hello</b>");
});
</script>
<style>p { background:yellow; }</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>I would like to say: </p>
</body>
</html>
6. appendTo( content ) Returns: jQuery
appendTo( content ), 실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Append all of the matched elements to another, specified, set of elements.
매치되어진 원소들의 내용들을 주어진 조건에 맞는 원소에 추가로 삽입한후 객체 반환
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("span").appendTo("#foo"); // check append() examples
});
</script>
<style>#foo { background:yellow; }</style>
</head>
<body>
<span>I have nothing more to say... </span>
<div id="foo">FOO! </div>
</body>
</html>
7. prepend( content ) Returns: jQuery
prepend( content ), 실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Prepend content to the inside of every matched element.
매치되어진 원소들에 맨앞에 주어진 내용을 삽입한후 객체를 반환
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("p").prepend("<b>Hello </b>");
});
</script>
<style>p { background:yellow; }</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>there friend!</p>
<p>amigo!</p>
</body>
</html>
8. prependTo( content ) Returns: jQuery
prependTo( content ) 실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Prepend all of the matched elements to another, specified, set of elements.
매칮되어진 원소의 내용을 주어진 것에 매치되는 원소의 맨앞에 추가 삽입한후 객체를 반환
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("span").prependTo("#foo"); // check prepend() examples
});
</script>
<style>div { background:yellow; }</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="foo">FOO!</div>
<span>I have something to say... </span>
</body>
</html>
9. after( content ) Returns: jQuery
after( content ), 실행후 jQuery 객체를 반환
Insert content after each of the matched elements.
매치되는 모든 원소의 뒤에 주어진 내용을 삽입
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("p").after("<b>Hello</b>");
});
</script>
<style>p { background:yellow; }</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>I would like to say: </p>
</body>
</html>
10. before( content ) Returns: jQuery
before( content ) 실행후 jQuery 객체를 반환
Insert content before each of the matched elements.
매치되는 모는 원소의 앞에 주어진 내용 삽입
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("p").before("<b>Hello</b>");
});
</script>
<style>p { background:yellow; }</style>
</head>
<body>
<p> is what I said...</p>
</body>
</html>
11. insertAfter( content ) Returns: jQuery
insertAfter( content ), 실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Insert all of the matched elements after another, specified, set of elements.
매치되어진 원소들을 주어진 것에 매치되는 원소의 뒤에 삽입한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("p").insertAfter("#foo"); // check after() examples
});
</script>
<style>#foo { background:yellow; }</style>
</head>
<body>
<p> is what I said... </p><div id="foo">FOO!</div>
</body>
</html>
12. insertBefore( content ) Returns: jQuery
insertBefore( content ), 실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Insert all of the matched elements before another, specified, set of elements.
매치되어진 원소앞에 주어진 것에 매치된 원소를 삽입한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("p").insertBefore("#foo"); // check before() examples
});
</script>
<style>#foo { background:yellow; }</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="foo">FOO!</div><p>I would like to say: </p>
</body>
</html>
13. wrap( html ) Returns: jQuery
wrap( html ), 실행후 jQuery 객체를 반환
Wrap all matched elements with a structure of other elements.
매치되어진 원소를 주어진 html로서 감싼후 객체를 반환
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("span").wrap("<div><div><p><em><b></b></em></p></div></div>");
});
</script>
<style>
div { border:2px blue solid; margin:2px; padding:2px; }
p { background:yellow; margin:2px; padding:2px; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<span>Span Text</span>
<span>Another One</span>
</body>
</html>
14. wrap( elem ) Returns: jQuery
wrap( elem ), 실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Wrap all matched elements with a structure of other elements.
매치된 모든 원소를 주어진것에 매치되는 원소로 감싼다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("p").wrap(document.getElementById('content'));
});
</script>
<style>#content { background:#9f9; }</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>Test Paragraph.</p><div id="content"></div>
</body>
</html>
15. wrapAll( html ) Returns: jQuery
wrapAll( html ) 실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Wrap all the elements in the matched set into a single wrapper element.
매치되는 원소들을 주어진 html로 모두 하나로 감싼다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("span").wrapAll("<div><div><p><em><b></b></em></p></div></div>");
});
</script>
<style>
div { border:2px blue solid; margin:2px; padding:2px; }
p { background:yellow; margin:2px; padding:2px; }
strong { color:red; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<span>Span Text</span>
<strong>What about me?</strong>
<span>Another One</span>
</body>
</html>
16. wrapAll( elem ) Returns: jQuery
wrapAll( elem ), 실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Wrap all the elements in the matched set into a single wrapper element.
매치되어진 원소들을 주어진 것에 매치되는 것으로 하나로 감싼다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("p").wrapAll(document.createElement("div"));
});
</script>
<style>
div { border: 2px solid blue; }
p { background:yellow; margin:4px; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>Hello</p>
<p>cruel</p>
<p>World</p>
</body>
</html>
17. wrapInner( html ) Returns: jQuery
wrapInner( html ), 실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Wrap the inner child contents of each matched element (including text nodes) with an HTML structure.
매치되어진 원소 속의 내용을 주어진 것으로 감싼다
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("body").wrapInner("<div><div><p><em><b></b></em></p></div></div>");
});
</script>
<style>
div { border:2px green solid; margin:2px; padding:2px; }
p { background:yellow; margin:2px; padding:2px; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
Plain old text, or is it?
</body>
</html>
18. wrapInner( elem ) Returns: jQuery
wrapInner( elem ), 실행후 jQuery 객체를 반환
Wrap the inner child contents of each matched element (including text nodes) with a DOM element.
매치되어진 원소 속의 내용을 주어진 것에 매치된것으로 감싼다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("p").wrapInner(document.createElement("b"));
});
</script>
<style>p { background:#9f9; }</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>Hello</p>
<p>cruel</p>
<p>World</p>
</body>
</html>
19. replaceWith( content ) Returns: jQuery
replaceWith( content ), 실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Replaces all matched elements with the specified HTML or DOM elements.
매치되어진 원소를 주어진 내용과 치환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("button").click(function () {
$(this).replaceWith("<div>" + $(this).text() + "</div>");
});
});
</script>
<style>
button { display:block; margin:3px; color:red; width:200px; }
div { color:red; border:2px solid blue; width:200px;
margin:3px; text-align:center; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<button>First</button>
<button>Second</button>
<button>Third</button>
</body>
</html>
20. replaceAll( selector ) Returns: jQuery
replaceAll( selector ), 실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Replaces the elements matched by the specified selector with the matched elements.
매치되어진 것들을 주어진 것에 매치되는 것에 모두 바꿈
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("<b>Paragraph. </b>").replaceAll("p"); // check replaceWith() examples
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<p>Hello</p>
<p>cruel</p>
<p>World</p>
</body>
</html>
21. empty( ) Returns: jQuery
empty( ) 실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Remove all child nodes from the set of matched elements.
매치되어진 모든 것들을 없앤다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("button").click(function () {
$("p").empty();
});
});
</script>
<style>
p { background:yellow; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>
Hello, <span>Person</span> <a href=";">and person</a>
</p>
<button>Call empty() on above paragraph</button>
</body>
</html>
22. remove( expr ) Returns: jQuery
remove( expr ), 실행후 jQuery 객체를 반환
Removes all matched elements from the DOM.
매치되는 모든 원소를 옮기다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("button").click(function () {
$("p").remove();
});
});
</script>
<style>p { background:yellow; margin:6px 0; }</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>Hello</p>
how are
<p>you?</p>
<button>Call remove() on paragraphs
</body>
</html>
23. clone( ) Returns: jQuery
clone( ) 실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Clone matched DOM Elements and select the clones.
선택되어진 원소를 복사
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("b").clone().prependTo("p");
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<b>Hello</b><p>, how are you?</p>
</body>
</html>
24. clone( true ) Returns: jQuery
clone( true ) 실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Clone matched DOM Elements, and all their event handlers, and select the clones.
완벽한 복사
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("button").click(function(){
$(this).clone(true).insertAfter(this);
});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<button>Clone Me!</button>
</body>
</html>
<CSS>
1. css( name ) Returns: String
css( name ) 실행후 문자열 반환
Return a style property on the first matched element.
매치된 원소에서 주어진 스타일 속성이 발견되면 그 값을 반환
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("div").click(function () {
var color = $(this).css("background-color");
$("#result").html("That div is <span style='color:" +
color + ";'>" + color + "</span>.");
});
});
</script>
<style>
div { width:60px; height:60px; margin:5px; float:left; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<span id="result"> </span>
<div style="background-color:blue;"></div>
<div style="background-color:rgb(15,99,30);"></div>
<div style="background-color:#123456;"></div>
<div style="background-color:#f11;"></div>
</body>
</html>
2. css( properties ) Returns: jQuery
css( properties ) 실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Set a key/value object as style properties to all matched elements.
매치되어진 모든 원소에 주어진 키와 값으로 이루어진 속성들의 배열의 스타일을 적용하고 객체를 반환
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("p").hover(function () {
$(this).css({ "background-color":"yellow", "font-weight":"bolder" });
}, function () {
var cssObj = {
"background-color": "#ddd",
"font-weight": "",
color: "rgb(0,40,244)"
}
$(this).css(cssObj);
});
});
</script>
<style>
p { color:green; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>
Move the mouse over a paragraph.
</p>
<p>
Like this one or the one above.
</p>
</body>
</html>
3. css( name, value ) Returns: jQuery
css( name, value ) 실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Set a single style property to a value on all matched elements.
하나의 속성과 값을 받아 매치되어진 모든 원소에 적용
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("p").mouseover(function () {
$(this).css("color","red");
});
});
</script>
<style>
p { color:blue; width:200px; font-size:14px; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>
Just roll the mouse over me.
</p>
<p>
Or me to see a color change.
</p>
</body>
</html>
4. offset( ) Returns: Object{top,left}
offset( ) 실행후 탑과 레프트에 해당하는 위치 정보를 반환
Get the current offset of the first matched element relative to the viewport.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
var p = $("p:last");
var offset = p.offset();
p.html( "left: " + offset.left + ", top: " + offset.top );
});
</script>
<style>
p { margin-left:10px; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>Hello</p><p>2nd Paragraph</p>
</body>
</html>
5. height( ) Returns: Integer
height( ) 실행후 정수형을 반환한다.
Get the current computed, pixel, height of the first matched element.
매치된 첫번째 원소의 높이를 픽셀로 반환한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
function showHeight(ele, h) {
$("div").text("The height for the " + ele +
" is " + h + "px.");
}
$("#getp").click(function () {
showHeight("paragraph", $("p").height());
});
$("#getd").click(function () {
showHeight("document", $(document).height());
});
$("#getw").click(function () {
showHeight("window", $(window).height());
});
});
</script>
<style>
body { background:yellow; }
button { font-size:12px; margin:2px; }
p { width:150px; border:1px red solid; }
div { color:red; font-weight:bold; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<button id="getp">Get Paragraph Height</button>
<button id="getd">Get Document Height</button>
<button id="getw">Get Window Height</button>
<div> </div>
<p>
Sample paragraph to test height
</p>
</body>
</html>
6. height( val ) Returns: jQuery
height( val ) 실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Set the CSS height of every matched element.
매치되는 모든 원소에 주어진 높이를 적용한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("div").one('click', function () {
$(this).height(30)
.css({cursor:"auto", backgroundColor:"green"});
});
});
</script>
<style>
div { width:50px; height:70px; float:left; margin:5px;
background:rgb(255,140,0); cursor:pointer; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
7. width( ) Returns: Integer
width( ) 실행후 정수형을 반환
Get the current computed, pixel, width of the first matched element.
매치되는 첫번째 원소의 너비를 픽셀로 반환
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
function showWidth(ele, w) {
$("div").text("The width for the " + ele +
" is " + w + "px.");
}
$("#getp").click(function () {
showWidth("paragraph", $("p").width());
});
$("#getd").click(function () {
showWidth("document", $(document).width());
});
$("#getw").click(function () {
showWidth("window", $(window).width());
});
});
</script>
<style>
body { background:yellow; }
button { font-size:12px; margin:2px; }
p { width:150px; border:1px red solid; }
div { color:red; font-weight:bold; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<button id="getp">Get Paragraph Width</button>
<button id="getd">Get Document Width</button>
<button id="getw">Get Window Width</button>
<div> </div>
<p>
Sample paragraph to test width
</p>
</body>
</html>
8. width( val ) Returns: jQuery
width( val ) 실행후 jQuery 객체를 반환
Set the CSS width of every matched element.
매치되는 모든 원소에 주어진 너비를 적용한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("div").one('click', function () {
$(this).width(30)
.css({cursor:"auto", "background-color":"blue"});
});
});
</script>
<style>
div { width:70px; height:50px; float:left; margin:5px;
background:red; cursor:pointer; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
<Events>
1. ready( fn ) Returns: jQuery
ready( fn ) 실행후 jQuery 객체를 반환
Binds a function to be executed whenever the DOM is ready to be traversed and manipulated.
문서가 준비가 되면 그 시점에 함수를 실행시킨다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("p").text("The DOM is now loaded and can be manipulated.");
});
</script>
<style>p { color:red; }</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>
</p>
</body>
</html>
2. bind( type, data, fn ) Returns: jQuery
bind( type, data, fn ) 실행후 jQuery 객체를 반환
Binds a handler to a particular event (like click) for each matched element.
지정된 이벤트가 일어날때까지 기다렷다가 함수 실행
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("p").bind("click", function(e){
var str = "( " + e.pageX + ", " + e.pageY + " )";
$("span").text("Click happened! " + str);
});
$("p").bind("dblclick", function(){
$("span").text("Double-click happened in " + this.tagName);
});
});
</script>
<style>
p { background:yellow; font-weight:bold; cursor:pointer;
padding:5px; }
span { color:red; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>Click or double click here.</p>
<span></span>
</body>
</html>
3. one( type, data, fn ) Returns: jQuery
one( type, data, fn ) 실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Binds a handler to a particular event to be executed once for each matched element.
지정된 이벤트가 일어날때까지 기다렷다가 한번만 실행
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
var n = 0;
$("div").one("click", function(){
var index = $("div").index(this);
$(this).css({ borderStyle:"inset",
cursor:"auto" });
$("p").text("Div at index #" + index + " clicked." +
" That's " + ++n + " total clicks.");
});
});
</script>
<style>
div { width:60px; height:60px; margin:5px; float:left;
background:green; border:10px outset;
cursor:pointer; }
p { color:red; margin:0; clear:left; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<p>Click a green square...</p>
</body>
</html>
4. trigger( type, data ) Returns: jQuery
trigger( type, data ) 실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Trigger a type of event on every matched element.
매치되는 모든 원소에 지정된 타입의 이벤트를 발생시킨다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("button:first").click(function () {
update($("span:first"));
});
$("button:last").click(function () {
$("button:first").trigger('click');
update($("span:last"));
});
function update(j) {
var n = parseInt(j.text(), 0);
j.text(n + 1);
}
});
</script>
<style>
button { margin:10px; }
div { color:blue; font-weight:bold; }
span { color:red; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<button>Button #1</button>
<button>Button #2</button>
<div><span>0</span> button #1 clicks.</div>
<div><span>0</span> button #2 clicks.</div>
</body>
</html>
5. triggerHandler( type, data ) Returns: jQuery
triggerHandler( type, data ) 실행후 jQuery객체 반환
This particular method triggers all bound event handlers on an element (for a specific event type) WITHOUT executing the browsers default actions.
잘은 모르겟지만 실제적인 행위는 하지 않고 그결과만 실행한다는 뜻인것 같음
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("#old").click(function(){
$("input").trigger("focus");
});
$("#new").click(function(){
$("input").triggerHandler("focus");
});
$("input").focus(function(){
$("<span>Focused!</span>").appendTo("body").fadeOut(1000);
});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<button id="old">.trigger("focus")</button>
<button id="new">.triggerHandler("focus")</button><br/><br/>
<input type="text" value="To Be Focused"/>
</body>
</html>
6. unbind( type, data ) Returns: jQuery
unbind( type, data ), 실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
This does the opposite of bind, it removes bound events from each of the matched elements.
bind와 정반대의 역활을 하며 매치되는 모든 원소에 바운드 이벤트를 제거한다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
function aClick() {
$("div").show().fadeOut("slow");
}
$("#bind").click(function () {
// could use .bind('click', aClick) instead but for variety...
$("#theone").click(aClick)
.text("Can Click!");
});
$("#unbind").click(function () {
$("#theone").unbind('click', aClick)
.text("Does nothing...");
});
});
</script>
<style>
button { margin:5px; }
button#theone { color:red; background:yellow; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<button id="theone">Does nothing...</button>
<button id="bind">Bind Click</button>
<button id="unbind">Unbind Click</button>
<div style="display:none;">Click!</div>
</body>
</html>
7. hover( over, out ) Returns: jQuery
hover( over, out ) 실행후 jQuery 객체를 반환
Simulates hovering (moving the mouse on, and off, an object). This is a custom method which provides an 'in' to a frequent task.
마우스 오버와 아웃시 행위를 지정할수 있다.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("li").hover(
function () {
$(this).append($("<span> ***</span>"));
},
function () {
$(this).find("span:last").remove();
}
);
});
</script>
<style>
ul { margin-left:20px; color:blue; }
li { cursor:default; }
span { color:red; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li>Milk</li>
<li>Bread</li>
<li>Chips</li>
<li>Socks</li>
</ul>
</body>
8. toggle( fn, fn ) Returns: jQuery
toggle( fn, fn ) 실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Toggle between two function calls every other click.
클릭시 두개의 함수를 반복적으로 실행
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("li").toggle(
function () {
$(this).css("list-style-type", "disc")
.css("color", "blue");
},
function () {
$(this).css({"list-style-type":"", "color":""});
}
);
});
</script>
<style>
ul { margin:10px; list-style:inside circle; font-weight:bold; }
li { cursor:pointer; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li>Go to the store</li>
<li>Pick up dinner</li>
<li>Debug crash</li>
<li>Take a jog</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
9. blur( ) Returns: jQuery
blur( ) 실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Triggers the blur event of each matched element.
10. blur( fn ) Returns: jQuery
blur( fn ) 실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Bind a function to the blur event of each matched element.
11. change( ) Returns: jQuery
change( ) 실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Triggers the change event of each matched element.
12. change( fn ) Returns: jQuery
change( fn ) 실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Binds a function to the change event of each matched element.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("select").change(function () {
var str = "";
$("select option:selected").each(function () {
str += $(this).text() + " ";
});
$("div").text(str);
})
.change();
});
</script>
<style>
div { color:red; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<select name="sweets" multiple="multiple">
<option>Chocolate</option>
<option selected="selected">Candy</option>
<option>Taffy</option>
<option selected="selected">Carmel</option>
<option>Fudge</option>
<option>Cookie</option>
</select>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
13. click( ) Returns: jQuery
click( ) 실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Triggers the click event of each matched element.
14. click( fn ) Returns: jQuery
click( fn ) 실행후 jQuery 객체 반환
Binds a function to the click event of each matched element.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("p").click(function () {
$(this).slideUp();
});
$("p").hover(function () {
$(this).addClass("hilite");
}, function () {
$(this).removeClass("hilite");
});
});
</script>
<style>
p { color:red; margin:5px; cursor:pointer; }
p.hilite { background:yellow; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>First Paragraph</p>
<p>Second Paragraph</p>
<p>Yet one more Paragraph</p>
</body>
</html>
15. dblclick( ) Returns: jQuery
dblclick( ) 실행후 jQuery 객체를 리턴
Triggers the dblclick event of each matched element.
16. dblclick( fn ) Returns: jQuery
dblclick( fn ) 실행후 jQuery 객체를 리턴
Binds a function to the dblclick event of each matched element.
17. error( ) Returns: jQuery
Triggers the error event of each matched element.
18. error( fn ) Returns: jQuery
Binds a function to the error event of each matched element.
19. focus( ) Returns: jQuery
Triggers the focus event of each matched element.
20. focus( fn ) Returns: jQuery
Binds a function to the focus event of each matched element.
21. keydown( ) Returns: jQuery
Triggers the keydown event of each matched element.
22. keydown( fn ) Returns: jQuery
Bind a function to the keydown event of each matched element.
23. keypress( ) Returns: jQuery
Triggers the keypress event of each matched element.
24. keypress( fn ) Returns: jQuery
Binds a function to the keypress event of each matched element.
25. keyup( ) Returns: jQuery
Triggers the keyup event of each matched element.
26. keyup( fn ) Returns: jQuery
Bind a function to the keyup event of each matched element.
27. load( fn ) Returns: jQuery
Binds a function to the load event of each matched element.
28. mousedown( fn ) Returns: jQuery
Binds a function to the mousedown event of each matched element.
29. mousemove( fn ) Returns: jQuery
Bind a function to the mousemove event of each matched element.
30. mouseout( fn ) Returns: jQuery
Bind a function to the mouseout event of each matched element.
31. mouseover( fn ) Returns: jQuery
Bind a function to the mouseover event of each matched element.
32. mouseup( fn ) Returns: jQuery
Bind a function to the mouseup event of each matched element.
33. resize( fn ) Returns: jQuery
Bind a function to the resize event of each matched element.
34. scroll( fn ) Returns: jQuery
Bind a function to the scroll event of each matched element.
35. select( ) Returns: jQuery
Trigger the select event of each matched element.
36. select( fn ) Returns: jQuery
Bind a function to the select event of each matched element.
37. submit( ) Returns: jQuery
Trigger the submit event of each matched element.
38. submit( fn ) Returns: jQuery
Bind a function to the submit event of each matched element.
39. unload( fn ) Returns: jQuery
Binds a function to the unload event of each matched element.
<Effect>
1. show( ) Returns: jQuery
Displays each of the set of matched elements if they are hidden.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("p").show()
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<p style="display:none">Hello</p>
</body>
</html>
2. show( speed, callback ) Returns: jQuery
Show all matched elements using a graceful animation and firing an optional callback after completion.
##A string representing one of the three predefined speeds ("slow", "normal", or "fast") or the number of milliseconds to run the animation (e.g. 1000).
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("button").click(function () {
$("p").show("slow");
});
});
</script>
<style>
p { background:yellow; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<button>Show it</button>
<p style="display: none">Hello</p>
</body>
</html>
3. hide( ) Returns: jQuery
Hides each of the set of matched elements if they are shown.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("p").hide();
$("a").click(function () {
$(this).hide();
return false;
});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<p>Hello</p>
<a href="#">Click to hide me too</a>
<p>Here is another paragraph</p>
</body>
</html>
4. hide( speed, callback ) Returns: jQuery
Hide all matched elements using a graceful animation and firing an optional callback after completion.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("button").click(function () {
$("p").hide("slow");
});
});
</script>
<style>
p { background:#dad; font-weight:bold; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<button>Hide 'em</button>
<p>Hiya</p>
<p>Such interesting text, eh?</p>
</body>
</html>
5. toggle( ) Returns: jQuery
Toggles each of the set of matched elements.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("button").click(function () {
$("p").toggle();
});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<button>Toggle</button>
<p>Hello</p>
<p style="display: none">Good Bye</p>
</body>
</html>
6. slideDown( speed, callback ) Returns: jQuery
Reveal all matched elements by adjusting their height and firing an optional callback after completion.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$(document.body).click(function () {
if ($("div:first").is(":hidden")) {
$("div").slideDown("slow");
} else {
$("div").hide();
}
});
});
</script>
<style>
div { background:#de9a44; margin:3px; width:80px;
height:40px; display:none; float:left; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
Click me!
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
7. slideUp( speed, callback ) Returns: jQuery
Hide all matched elements by adjusting their height and firing an optional callback after completion.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$(document.body).click(function () {
if ($("div:first").is(":hidden")) {
$("div").show("fast");
} else {
$("div").slideUp();
}
});
});
</script>
<style>
div { background:#3d9a44; margin:3px; width:80px;
height:40px; float:left; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
Click me!
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
8. slideToggle( speed, callback ) Returns: jQuery
Toggle the visibility of all matched elements by adjusting their height and firing an optional callback after completion.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("button").click(function () {
$("p").slideToggle("slow");
});
});
</script>
<style>
p { width:400px; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<button>Toggle</button>
<p>
This is the paragraph to end all paragraphs. You
should feel <em>lucky</em> to have seen such a paragraph in
your life. Congratulations!
</p>
</body>
</html>
9. fadeIn( speed, callback ) Returns: jQuery
Fade in all matched elements by adjusting their opacity and firing an optional callback after completion.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$(document.body).click(function () {
$("div:hidden:first").fadeIn("slow");
});
});
</script>
<style>
span { color:red; cursor:pointer; }
div { margin:3px; width:80px; display:none;
height:80px; float:left; }
div#one { background:#f00; }
div#two { background:#0f0; }
div#three { background:#00f; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<span>Click here...</span>
<div id="one"></div>
<div id="two"></div>
<div id="three"></div>
</body>
</html>
10. fadeOut( speed, callback ) Returns: jQuery
Fade out all matched elements by adjusting their opacity and firing an optional callback after completion.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("p").click(function () {
$("p").fadeOut("slow");
});
});
</script>
<style>
p { font-size:150%; cursor:pointer; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>
If you click on this paragraph
you'll see it just fade away.
</p>
</body>
</html>
11. fadeTo( speed, opacity, callback ) Returns: jQuery
Fade the opacity of all matched elements to a specified opacity and firing an optional callback after completion.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("p:first").click(function () {
$(this).fadeTo("slow", 0.33);
});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<p>
Click this paragraph to see it fade.
</p>
<p>
Compare to this one that won't fade.
</p>
</body>
</html>
12. animate( params, duration, easing, callback ) Returns: jQuery
A function for making your own, custom animations.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("#right").click(function(){
$(".block").animate({"left": "+=50px"}, "slow");
});
$("#left").click(function(){
$(".block").animate({"left": "-=50px"}, "slow");
});
});
</script>
<style>
div {
position:absolute;
background-color:#abc;
left:50px;
width:90px;
height:90px;
margin:5px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<button id="left">≪</button> <button id="right">≫</button>
<div class="block"></div>
</body>
</html>
13. animate( params, options ) Returns: jQuery
A function for making your own, custom animations.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
// Using multiple unit types within one animation.
$("#go").click(function(){
$("#block").animate({
width: "70%",
opacity: 0.4,
marginLeft: "0.6in",
fontSize: "3em",
borderWidth: "10px"
}, 1500 );
});
});
</script>
<style>
div {
background-color:#bca;
width:100px;
border:1px solid green;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<button id="go">≫ Run</button>
<div id="block">Hello!</div>
</body>
</html>
14. stop( ) Returns: jQuery
Stops all the currently running animations on all the specified elements.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
// Start animation
$("#go").click(function(){
$(".block").animate({left: '+=100px'}, 2000);
});
// Stop animation when button is clicked
$("#stop").click(function(){
$(".block").stop();
});
// Start animation in the opposite direction
$("#back").click(function(){
$(".block").animate({left: '-=100px'}, 2000);
});
});
</script>
<style>div {
position: absolute;
background-color: #abc;
left: 0px;
top:30px;
width: 60px;
height: 60px;
margin: 5px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<button id="go">Go</button>
<button id="stop">STOP!</button>
<button id="back">Back</button>
<div class="block"></div>
</body>
</html>
15. queue( ) Returns: Array<Function>
Returns a reference to the first element's queue (which is an array of functions).
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("#show").click(function () {
var n = $("div").queue("fx");
$("span").text("Queue length is: " + n.length);
});
function runIt() {
$("div").show("slow");
$("div").animate({left:'+=200'},2000);
$("div").slideToggle(1000);
$("div").slideToggle("fast");
$("div").animate({left:'-=200'},1500);
$("div").hide("slow");
$("div").show(1200);
$("div").slideUp("normal", runIt);
}
runIt();
});
</script>
<style>
div { margin:3px; width:40px; height:40px;
position:absolute; left:0px; top:30px;
background:green; display:none; }
div.newcolor { background:blue; }
span { color:red; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<button id="show">Show Length of Queue</button>
<span></span>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
16. queue( callback )
Adds a new function, to be executed, onto the end of the queue of all matched elements.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$(document.body).click(function () {
$("div").show("slow");
$("div").animate({left:'+=200'},2000);
$("div").queue(function () {
$(this).addClass("newcolor");
$(this).dequeue();
});
$("div").animate({left:'-=200'},500);
$("div").queue(function () {
$(this).removeClass("newcolor");
$(this).dequeue();
});
$("div").slideUp();
});
});
</script>
<style>
div { margin:3px; width:40px; height:40px;
position:absolute; left:0px; top:30px;
background:green; display:none; }
div.newcolor { background:blue; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
Click here...
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
17. queue( queue )
Replaces the queue of all matched element with this new queue (the array of functions).
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("#start").click(function () {
$("div").show("slow");
$("div").animate({left:'+=200'},5000);
$("div").queue(function () {
$(this).addClass("newcolor");
$(this).dequeue();
});
$("div").animate({left:'-=200'},1500);
$("div").queue(function () {
$(this).removeClass("newcolor");
$(this).dequeue();
});
$("div").slideUp();
});
$("#stop").click(function () {
$("div").queue("fx", []);
$("div").stop();
});
});
</script>
<style>
div { margin:3px; width:40px; height:40px;
position:absolute; left:0px; top:30px;
background:green; display:none; }
div.newcolor { background:blue; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<button id="start">Start</button>
<button id="stop">Stop</button>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
18. dequeue( ) Returns: jQuery
Removes a queued function from the front of the queue and executes it.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("button").click(function () {
$("div").animate({left:'+=200px'}, 2000);
$("div").animate({top:'0px'}, 600);
$("div").queue(function () {
$(this).toggleClass("red");
$(this).dequeue();
});
$("div").animate({left:'10px', top:'30px'}, 700);
});
});
</script>
<style>
div { margin:3px; width:50px; position:absolute;
height:50px; left:10px; top:30px;
background-color:yellow; }
div.red { background-color:red; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<button>Start</button>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>


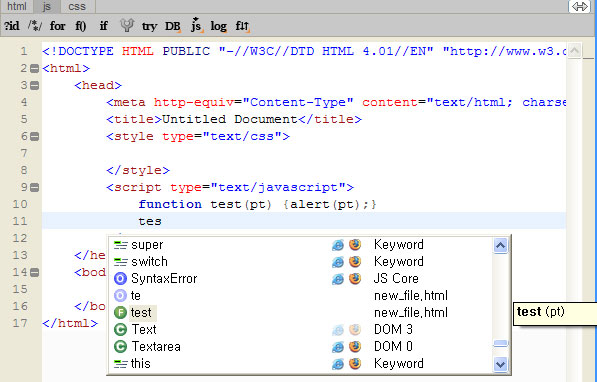

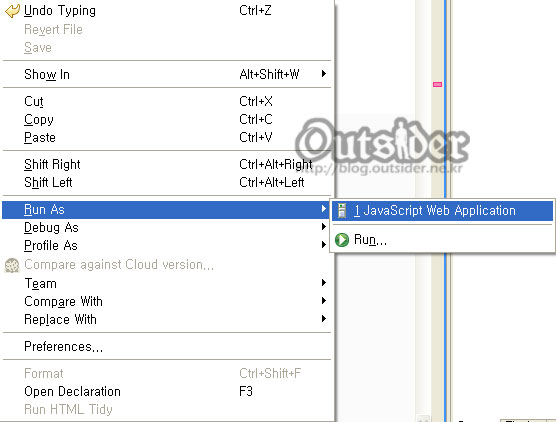

 Students.zip
Students.zip
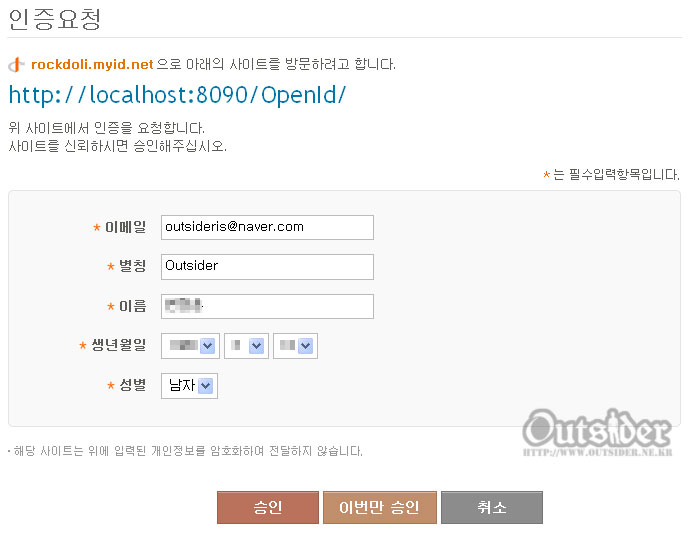

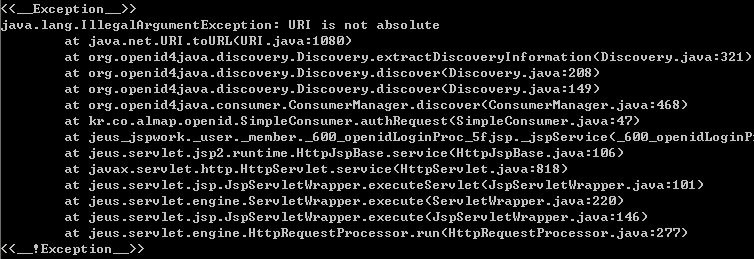


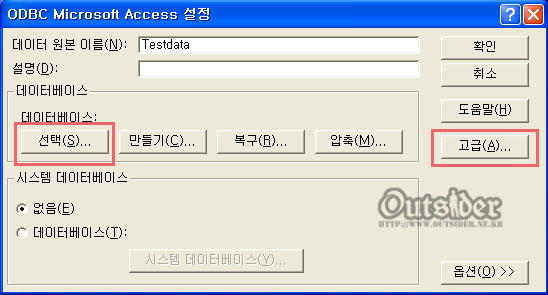
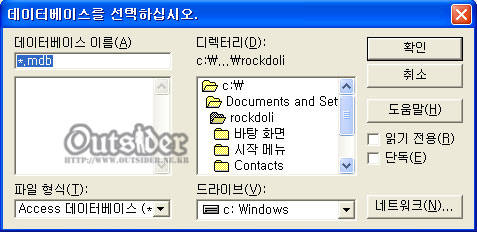
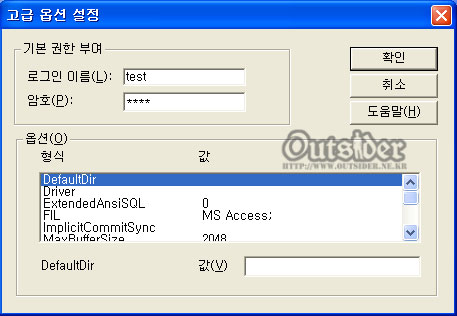

 If you submitted all homeworks - the deadline for the homework submission is Dec. 11th, 2009 -, please send an email to the
If you submitted all homeworks - the deadline for the homework submission is Dec. 11th, 2009 -, please send an email to the  ojdbc14.jar
ojdbc14.jar GEF-ALL-3.3.2.zip
GEF-ALL-3.3.2.zip